

Dec 19, 2025
Dec 19, 2025
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
ESG Strategy
ESG Strategy
In This Article
Select partnership impact tools—self-assessments, SNA, and evaluation models—to measure collaboration quality, ESG alignment, and financial & community outcomes.
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Partnership impact assessment tools help organizations evaluate collaboration quality and outcomes, going beyond basic metrics like financial results. These tools are particularly useful for U.S.-based nonprofits, public agencies, businesses, and other groups aiming to meet ESG goals or demonstrate measurable results to stakeholders. Key areas of focus include trust, communication, decision-making, and impacts like cost savings, emissions reductions, or community health improvements.
Key Takeaways:
Purpose: Assess both the process and results of partnerships, including social, environmental, and economic impacts.
Tool Selection: Match tools to your partnership's goals and stage (e.g., start-up, scaling, or renewal).
Implementation: Choose tools that fit your team's capacity and budget, and align with existing frameworks like ESG metrics.
Examples: Use models like the Partnership Impact Model™ for structured evaluations, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool for internal dynamics, or Social Network Analysis (SNA) for mapping relationships.
By integrating these tools into regular management practices, organizations can make better decisions, improve collaboration, and achieve measurable outcomes.
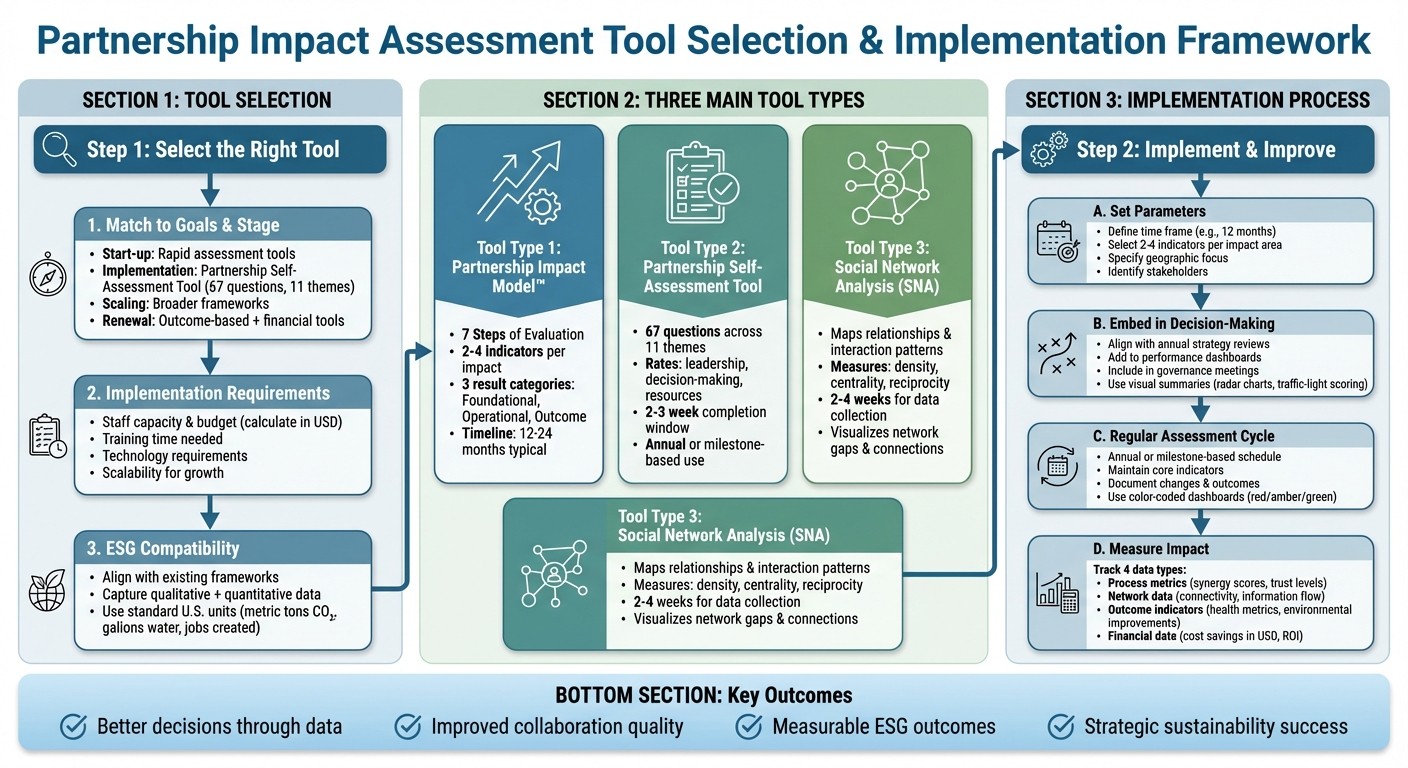
How to Select and Implement Partnership Impact Assessment Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide
Evaluation of Partnerships for Scaling


How to Select Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Before diving into tool selection, take a moment to clarify your primary goal. Are you performing a "health check" on your partnership, building a business case with ROI metrics, assessing systemic impact, or meeting ESG compliance requirements? Narrow down your options by eliminating tools that don’t align with your specific objective. Once you’ve identified potential tools, focus on three key factors: how well the tool matches your partnership type and lifecycle stage, your team’s capacity to use it effectively, and its compatibility with your current measurement frameworks.
Matching Tools to Partnership Goals and Stages
Partnerships naturally progress through different phases - design, implementation, scaling, or renewal - and each stage has unique measurement needs. The Partnership Impact Model™ can help you align these needs with appropriate tools. For example:
Start-up phase: Rapid assessment tools based on the six Partnership Principles can confirm foundational elements like governance structures and shared expectations.
Implementation phase: Tools such as the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool, which includes 67 questions across 11 themes, are ideal for monitoring collaboration quality and internal dynamics.
Scaling or systems change phase: Broader frameworks become necessary to measure large-scale impacts.
Renewal or close-out phase: Focus on outcome-based tools paired with financial evaluations to assess partner performance against set criteria.
A decision matrix that connects your goals - such as improving coordination, demonstrating community outcomes, or justifying investments - with available tools can simplify the selection process. This approach helps avoid over-measuring by identifying one or two complementary tools.
Implementation Requirements and Growth Capacity
Practical considerations play a critical role in determining a tool’s effectiveness. Short, straightforward instruments - like quick health-check questionnaires - are more likely to be completed by busy partners than lengthy surveys with 60+ questions. Tools using online platforms or simple spreadsheets are faster to deploy compared to those requiring specialized software. To minimize training time and errors, prioritize tools that come with clear user guides and scoring instructions.
When budgeting, calculate the required staff hours, consulting fees, and other costs in U.S. dollars to ensure the tool fits your financial constraints. For partnerships expecting to grow, look for modular tools or those with configurable criteria that can adapt to different organizational levels and partnership sizes. Some tools are specifically designed to identify areas of conflict and consensus among diverse participants, making them valuable in various contexts. Customizable tools can also be adjusted as partnerships evolve, and frameworks that categorize impacts into foundational, operational, and outcome areas can support both initial assessments and more advanced evaluations over time. Importantly, ensure the tool can scale with increasing data volumes without requiring major technological upgrades.
Compatibility with ESG and Sustainability Metrics
To fully evaluate a partnership’s impact, it’s essential to align your tools with existing ESG frameworks. These frameworks provide the structure for indicators and reporting, which is particularly important for organizations issuing sustainability reports or responding to investor inquiries. Tools rooted in multi-dimensional impact models - covering governance, operations, and outcomes - make it easier to connect partnership metrics to ESG categories.
Start by using partnership impact guides to identify and prioritize key impacts, then create specific indicators and metrics that align with ESG requirements. Choose tools that capture both qualitative and quantitative data, ensuring that the evidence gathered can be repurposed for ESG disclosures. For U.S.-based organizations, confirm that metrics can be expressed in commonly used units, such as metric tons of CO₂, gallons of water saved, or jobs created, and that they align with relevant U.S. regulatory or voluntary reporting standards. This alignment ensures your partnership assessments contribute meaningfully to your broader ESG and sustainability goals.
Partnership Impact Tools and Frameworks
When assessing partnerships, it's essential to identify your specific evaluation needs and select the right tools. Three primary options include structured evaluation models, self-assessment questionnaires, and network mapping methods. Each serves a unique purpose: evaluation models focus on tracking outcomes, self-assessment tools evaluate internal collaboration, and network mapping visualizes how individuals and organizations interact. These approaches build on earlier concepts, helping you choose the method that suits your partnership's dynamics.
Partnership Impact Evaluation Models
The 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation, part of the Partnership Impact Model™, offers a flexible framework for use throughout a partnership’s lifecycle. This process involves several stages: conceptualizing impacts, defining and prioritizing them with the Partnership Impact Roadmap, selecting methods and metrics (typically 2–4 indicators per impact), collecting and analyzing data, interpreting results, refining strategies, and evaluating outcomes. The model organizes results into three categories: foundational, operational, and outcome dimensions.
For example, a watershed partnership in the U.S. might begin by conceptualizing impacts like improved water quality, greater community involvement, and cost savings (measured in U.S. dollars). Over the next 12–24 months, they could prioritize specific indicators such as miles of stream restored, shifts in community satisfaction scores, or reductions in annual operating costs. Data collection might involve environmental monitoring and surveys, with results analyzed collaboratively to fine-tune strategies.[1][2]
While structured models offer a systematic approach, self-assessment tools provide valuable insights into the partnership’s internal workings.
Partnership Self-Assessment Tool
The Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is a detailed 67-question survey that evaluates partnership synergy - the added value generated when partners collaborate effectively.[3] Created by the Center for the Advancement of Collaborative Strategies in Health, the tool examines 11 key themes, including leadership, decision-making, resource contributions, and external factors. Respondents rate items using scales like "poor to excellent" or "none of the time to all of the time."
To use this tool, start by selecting the internal partnership to evaluate and identify participants, such as board members, managers, and frontline staff. The survey can be distributed electronically or on paper, with a 2–3 week completion window. Once responses are collected, scores are aggregated by theme to create profiles that reveal strengths and areas needing improvement. Teams can then hold discussions to interpret the results and set clear action plans with timelines and accountability. Conducting the assessment annually or at key milestones helps monitor progress and address issues early.[3]
Social Network Analysis (SNA)
Social Network Analysis (SNA) examines the relationships and interaction patterns within a partnership by using survey data and visualization tools.[1] This method measures attributes such as contact frequency, interaction types (e.g., information sharing or joint planning), trust levels, and the perceived value of relationships. Metrics like network density (overall connectivity), centrality (most influential members), and reciprocity (balance of two-way ties) provide valuable insights. It can also identify structural gaps, such as partners who may be under-connected.
To conduct an SNA, first define the network’s boundaries by deciding which individuals or organizations to include and what types of relationships to measure. A roster-based survey ensures comprehensive data collection, capturing details like contact frequency (daily, weekly, or monthly), trust levels, and the importance of ties. Allow 2–4 weeks for responses, with reminders to encourage participation. Use network mapping software to create visual representations where nodes symbolize organizations and lines represent relationships. Additional visual elements, such as color or size, can highlight factors like role, sector, or influence. These visualizations can then be reviewed in facilitated sessions to guide decisions about governance, equity, and resource allocation. For instance, the analysis might reveal over-reliance on a few central organizations or identify isolated partners who need greater engagement.[1]
Implementing Partnership Assessment Tools
To effectively implement partnership assessment tools, start by clarifying the purpose of your evaluation. Are you justifying funding, improving performance, or considering renewal? Pinpoint your partnership's current lifecycle stage - whether it's in the start-up phase, experiencing growth, well-established, or nearing its conclusion - as the tools and metrics you use will vary depending on this stage. Identify who will use the results, such as internal leaders, partner organizations, community representatives, or funders, and determine how the findings will guide decisions. For example, they might inform adjustments to governance structures or changes to cost-sharing models.
Taking these steps ensures that the assessment directly supports strategic decision-making.
Setting Evaluation Parameters
Translate your partnership's goals into specific impact areas using frameworks like the 11 Partnership Impacts and 7 Steps Evaluation. For each impact area, select 2–4 measurable indicators. These might include shifts in partner satisfaction scores, the number of shared initiatives launched, or progress in outcome metrics like reduced emissions or improved service access.
Define clear boundaries for the evaluation by specifying the time frame (e.g., 12 months), geographic focus (such as U.S. regions), and the partners and activities that will be assessed. Choose methods and metrics that align with the type of data you collect. For instance, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is ideal for evaluating relationship quality, while Social Network Analysis works well for mapping information flows and network structures. Ensure that the tool you choose supports your data formats - whether surveys, interviews, financial records, or ESG metrics - and that its outputs, such as scores or network diagrams, are easy for leadership to understand and act upon.
Embedding Tools in Decision-Making
To maximize impact, align assessment cycles with existing processes like annual strategy reviews, budget planning, or performance management meetings. This ensures that partnership metrics are reviewed alongside financial and operational data. Incorporate these indicators into performance dashboards or ESG reports so leadership can regularly monitor partnership health, rather than addressing it only during annual reviews. Regular governance meetings can also include partnership "check-ups", providing a structured opportunity to discuss strengths, gaps, and action steps.
Set clear thresholds that trigger reviews and link findings to specific decisions. For assessments involving input from multiple partners, use visual summaries like radar charts or traffic-light scoring systems during facilitated sessions to identify discrepancies in ratings and explore the reasons behind them. Present results as opportunities for growth rather than criticism, and collaborate with partners to create action plans targeting areas like data sharing, joint planning, or funding stability.
Embedding these tools into decision-making routines ensures they drive meaningful improvements.
Applying Tools Repeatedly for Improvement
Establish a regular assessment schedule, whether annually or tied to key project milestones. Each cycle should follow a consistent process: reconfirm impact areas, update methods and metrics if necessary, collect and analyze data, interpret findings, adapt strategies, and re-evaluate. While maintaining a core set of indicators - such as overall partnership synergy, financial impact, and community outcomes - consider adding or retiring metrics as the partnership evolves.
Document how previous assessments have led to tangible changes, such as updates to governance structures, improved communication practices, or revised cost-sharing models. Evaluate whether these changes have resulted in better outcomes. Use concise dashboards that combine numeric scores, color-coded indicators (e.g., red/amber/green thresholds), and brief narrative summaries to make results accessible and actionable for executives and funders. For audiences focused on financial and ESG outcomes, include quantified impacts like cost savings in dollars, revenue growth, or measurable social and environmental benefits, alongside qualitative insights from partners.
How Council Fire Supports Partnership Impact Assessment

Council Fire uses its expertise in sustainability to transform partnership evaluations into strategic tools for success. Serving governments, nonprofits, foundations, and private companies, they create assessment systems that connect partnership performance directly to measurable environmental, social, and financial outcomes.
Aligning Tools with Organizational Goals
Council Fire tailors its assessment frameworks to align with an organization’s strategy, ESG commitments, and partnership objectives. By mapping these elements to a clear theory of change, they help organizations turn broad priorities - like reducing watershed pollution or boosting community resilience - into concrete, measurable outputs and outcomes. For example, if a company aims to cut nutrient loads in a regional watershed, Council Fire develops dashboards that show how each partnership contributes to this goal. These dashboards integrate enterprise KPIs and ESG frameworks, ensuring performance metrics align with both financial and environmental benchmarks.
This alignment not only provides clarity but also lays the groundwork for stronger stakeholder collaboration and customized solutions.
Engaging Stakeholders for Comprehensive Analysis
A successful assessment requires perspectives from all key players - executives, program managers, community groups, and technical experts. Council Fire facilitates this process through workshops, surveys, and structured interviews, gathering honest feedback on partnerships. They adapt self-assessment tools to let stakeholders rate aspects like communication, decision-making, and value creation on clear scales. These responses are then aggregated to uncover areas of agreement and potential conflict.
Additionally, Council Fire employs social network analysis (SNA) to map information flow within partnerships. SNA helps identify weaknesses, bottlenecks, and opportunities to strengthen connections. By combining these insights with qualitative feedback, they provide actionable recommendations to improve governance, streamline operations, and enhance resource allocation.
This comprehensive approach ensures that stakeholder input directly informs the design of actionable solutions.
Crafting Tailored Solutions
When off-the-shelf tools fall short, Council Fire develops custom solutions that blend impact models, self-assessments, and outcome tracking. For instance, they might create a scoring framework that balances factors like climate resilience, equity outcomes, regulatory compliance, and financial performance. These tools often include automated features, such as color-coded thresholds, to make performance levels easy to interpret. Council Fire also trains internal teams to use these tools effectively, ensuring they remain scalable as partnership portfolios grow.
Their approach includes structured annual reviews and midyear check-ins, creating a feedback loop that allows partnerships to adapt to evolving goals. This process refines partnership roles, sharpens focus, and directs investments where they can have the greatest impact.
Conclusion
Choose impact tools that align with your partnership's purpose and development stage, while also considering budget constraints, staff capacity, and ESG requirements. The best strategies blend quantitative methods with qualitative insights. For instance, models like the 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation can work hand-in-hand with tools such as self-assessment questionnaires and social network analysis to evaluate measurable outcomes alongside relationship dynamics.
Data-driven collaboration transforms vague commitments into tangible progress across environmental, social, and financial goals. By analyzing diverse data types - process metrics (e.g., synergy scores and trust levels), network data (e.g., connectivity and information flow), outcome indicators (e.g., community health metrics and environmental improvements), and financial data (e.g., cost savings and return on collaboration) - partners gain a clear, evidence-based foundation for decision-making, moving beyond assumptions.
Incorporating assessments into regular management routines ensures that data informs funding priorities and strategic decisions. Conducting thorough evaluations annually, supplemented by shorter reviews every six to twelve months, allows partnerships to refine their indicators as they evolve. This continuous process paves the way for tailored expert support.
Expert guidance can accelerate progress by clarifying impact objectives, customizing tools for specific sectors, leading stakeholder workshops, and building internal capacity for assessments. Organizations like Council Fire specialize in connecting financial performance with environmental and social outcomes, enabling partners to tie their metrics directly to sustainable, long-term success.
Following an assessment, convene a workshop with key stakeholders to identify three to five actionable improvements. Assign responsibilities, set clear deadlines, update dashboards, and share results with funders. This ongoing cycle of evaluation and refinement strengthens strategic sustainability efforts and drives meaningful, lasting impact.
FAQs
What’s the best way to select a partnership impact assessment tool for my organization?
Choosing a partnership impact assessment tool begins with a clear understanding of your organization’s goals and the specific outcomes you aim to evaluate. Key considerations include how well the tool fits your industry, its user-friendliness, the types of data it requires, and its compatibility with your existing systems.
It’s also important to focus on the kind of insights you need to inform impactful decisions. Seeking advice from professionals, like the experts at Council Fire, can be incredibly helpful in ensuring the tool aligns with your sustainability and impact goals, particularly when adhering to U.S. standards and metrics.
What are the main stages of evaluating a partnership, and which tools are most effective for each?
When assessing a partnership, the process generally unfolds in three key phases:
Setting Objectives and Assessing Impact: This involves clarifying goals and using tools such as impact metrics and stakeholder analysis. These help ensure that all parties are aligned and that potential outcomes are carefully evaluated.
Strategic Planning and Execution: Here, decision-making frameworks and systems thinking come into play. These approaches guide resource allocation and help outline a clear, actionable roadmap for achieving shared objectives.
Ongoing Evaluation and Adjustment: Impact measurement tools are crucial in this stage. They allow for tracking progress, sharing insights, and making necessary adjustments to strategies to stay responsive to changing circumstances.
By following these steps, partnerships can achieve results that are both measurable and meaningful, while remaining flexible to meet new challenges or opportunities.
How can partnership impact assessments support ESG and sustainability goals?
To align partnership impact assessments with ESG and sustainability goals, it's essential to establish clear, measurable metrics that represent your environmental, social, and governance priorities. These metrics should account for both immediate results and long-term effects, such as fostering resilience and supporting ecosystem health.
Involve stakeholders at every stage to ensure the assessment mirrors shared values and promotes collaboration. The insights gained can guide strategic decisions, monitor progress, and uphold accountability. Adding storytelling to the mix can help convey achievements effectively and inspire continued dedication to sustainability objectives.
Related Blog Posts

Latest Articles
©2025
FAQ
FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Dec 19, 2025
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
ESG Strategy
In This Article
Select partnership impact tools—self-assessments, SNA, and evaluation models—to measure collaboration quality, ESG alignment, and financial & community outcomes.
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Partnership impact assessment tools help organizations evaluate collaboration quality and outcomes, going beyond basic metrics like financial results. These tools are particularly useful for U.S.-based nonprofits, public agencies, businesses, and other groups aiming to meet ESG goals or demonstrate measurable results to stakeholders. Key areas of focus include trust, communication, decision-making, and impacts like cost savings, emissions reductions, or community health improvements.
Key Takeaways:
Purpose: Assess both the process and results of partnerships, including social, environmental, and economic impacts.
Tool Selection: Match tools to your partnership's goals and stage (e.g., start-up, scaling, or renewal).
Implementation: Choose tools that fit your team's capacity and budget, and align with existing frameworks like ESG metrics.
Examples: Use models like the Partnership Impact Model™ for structured evaluations, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool for internal dynamics, or Social Network Analysis (SNA) for mapping relationships.
By integrating these tools into regular management practices, organizations can make better decisions, improve collaboration, and achieve measurable outcomes.

How to Select and Implement Partnership Impact Assessment Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide
Evaluation of Partnerships for Scaling

How to Select Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Before diving into tool selection, take a moment to clarify your primary goal. Are you performing a "health check" on your partnership, building a business case with ROI metrics, assessing systemic impact, or meeting ESG compliance requirements? Narrow down your options by eliminating tools that don’t align with your specific objective. Once you’ve identified potential tools, focus on three key factors: how well the tool matches your partnership type and lifecycle stage, your team’s capacity to use it effectively, and its compatibility with your current measurement frameworks.
Matching Tools to Partnership Goals and Stages
Partnerships naturally progress through different phases - design, implementation, scaling, or renewal - and each stage has unique measurement needs. The Partnership Impact Model™ can help you align these needs with appropriate tools. For example:
Start-up phase: Rapid assessment tools based on the six Partnership Principles can confirm foundational elements like governance structures and shared expectations.
Implementation phase: Tools such as the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool, which includes 67 questions across 11 themes, are ideal for monitoring collaboration quality and internal dynamics.
Scaling or systems change phase: Broader frameworks become necessary to measure large-scale impacts.
Renewal or close-out phase: Focus on outcome-based tools paired with financial evaluations to assess partner performance against set criteria.
A decision matrix that connects your goals - such as improving coordination, demonstrating community outcomes, or justifying investments - with available tools can simplify the selection process. This approach helps avoid over-measuring by identifying one or two complementary tools.
Implementation Requirements and Growth Capacity
Practical considerations play a critical role in determining a tool’s effectiveness. Short, straightforward instruments - like quick health-check questionnaires - are more likely to be completed by busy partners than lengthy surveys with 60+ questions. Tools using online platforms or simple spreadsheets are faster to deploy compared to those requiring specialized software. To minimize training time and errors, prioritize tools that come with clear user guides and scoring instructions.
When budgeting, calculate the required staff hours, consulting fees, and other costs in U.S. dollars to ensure the tool fits your financial constraints. For partnerships expecting to grow, look for modular tools or those with configurable criteria that can adapt to different organizational levels and partnership sizes. Some tools are specifically designed to identify areas of conflict and consensus among diverse participants, making them valuable in various contexts. Customizable tools can also be adjusted as partnerships evolve, and frameworks that categorize impacts into foundational, operational, and outcome areas can support both initial assessments and more advanced evaluations over time. Importantly, ensure the tool can scale with increasing data volumes without requiring major technological upgrades.
Compatibility with ESG and Sustainability Metrics
To fully evaluate a partnership’s impact, it’s essential to align your tools with existing ESG frameworks. These frameworks provide the structure for indicators and reporting, which is particularly important for organizations issuing sustainability reports or responding to investor inquiries. Tools rooted in multi-dimensional impact models - covering governance, operations, and outcomes - make it easier to connect partnership metrics to ESG categories.
Start by using partnership impact guides to identify and prioritize key impacts, then create specific indicators and metrics that align with ESG requirements. Choose tools that capture both qualitative and quantitative data, ensuring that the evidence gathered can be repurposed for ESG disclosures. For U.S.-based organizations, confirm that metrics can be expressed in commonly used units, such as metric tons of CO₂, gallons of water saved, or jobs created, and that they align with relevant U.S. regulatory or voluntary reporting standards. This alignment ensures your partnership assessments contribute meaningfully to your broader ESG and sustainability goals.
Partnership Impact Tools and Frameworks
When assessing partnerships, it's essential to identify your specific evaluation needs and select the right tools. Three primary options include structured evaluation models, self-assessment questionnaires, and network mapping methods. Each serves a unique purpose: evaluation models focus on tracking outcomes, self-assessment tools evaluate internal collaboration, and network mapping visualizes how individuals and organizations interact. These approaches build on earlier concepts, helping you choose the method that suits your partnership's dynamics.
Partnership Impact Evaluation Models
The 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation, part of the Partnership Impact Model™, offers a flexible framework for use throughout a partnership’s lifecycle. This process involves several stages: conceptualizing impacts, defining and prioritizing them with the Partnership Impact Roadmap, selecting methods and metrics (typically 2–4 indicators per impact), collecting and analyzing data, interpreting results, refining strategies, and evaluating outcomes. The model organizes results into three categories: foundational, operational, and outcome dimensions.
For example, a watershed partnership in the U.S. might begin by conceptualizing impacts like improved water quality, greater community involvement, and cost savings (measured in U.S. dollars). Over the next 12–24 months, they could prioritize specific indicators such as miles of stream restored, shifts in community satisfaction scores, or reductions in annual operating costs. Data collection might involve environmental monitoring and surveys, with results analyzed collaboratively to fine-tune strategies.[1][2]
While structured models offer a systematic approach, self-assessment tools provide valuable insights into the partnership’s internal workings.
Partnership Self-Assessment Tool

The Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is a detailed 67-question survey that evaluates partnership synergy - the added value generated when partners collaborate effectively.[3] Created by the Center for the Advancement of Collaborative Strategies in Health, the tool examines 11 key themes, including leadership, decision-making, resource contributions, and external factors. Respondents rate items using scales like "poor to excellent" or "none of the time to all of the time."
To use this tool, start by selecting the internal partnership to evaluate and identify participants, such as board members, managers, and frontline staff. The survey can be distributed electronically or on paper, with a 2–3 week completion window. Once responses are collected, scores are aggregated by theme to create profiles that reveal strengths and areas needing improvement. Teams can then hold discussions to interpret the results and set clear action plans with timelines and accountability. Conducting the assessment annually or at key milestones helps monitor progress and address issues early.[3]
Social Network Analysis (SNA)
Social Network Analysis (SNA) examines the relationships and interaction patterns within a partnership by using survey data and visualization tools.[1] This method measures attributes such as contact frequency, interaction types (e.g., information sharing or joint planning), trust levels, and the perceived value of relationships. Metrics like network density (overall connectivity), centrality (most influential members), and reciprocity (balance of two-way ties) provide valuable insights. It can also identify structural gaps, such as partners who may be under-connected.
To conduct an SNA, first define the network’s boundaries by deciding which individuals or organizations to include and what types of relationships to measure. A roster-based survey ensures comprehensive data collection, capturing details like contact frequency (daily, weekly, or monthly), trust levels, and the importance of ties. Allow 2–4 weeks for responses, with reminders to encourage participation. Use network mapping software to create visual representations where nodes symbolize organizations and lines represent relationships. Additional visual elements, such as color or size, can highlight factors like role, sector, or influence. These visualizations can then be reviewed in facilitated sessions to guide decisions about governance, equity, and resource allocation. For instance, the analysis might reveal over-reliance on a few central organizations or identify isolated partners who need greater engagement.[1]
Implementing Partnership Assessment Tools
To effectively implement partnership assessment tools, start by clarifying the purpose of your evaluation. Are you justifying funding, improving performance, or considering renewal? Pinpoint your partnership's current lifecycle stage - whether it's in the start-up phase, experiencing growth, well-established, or nearing its conclusion - as the tools and metrics you use will vary depending on this stage. Identify who will use the results, such as internal leaders, partner organizations, community representatives, or funders, and determine how the findings will guide decisions. For example, they might inform adjustments to governance structures or changes to cost-sharing models.
Taking these steps ensures that the assessment directly supports strategic decision-making.
Setting Evaluation Parameters
Translate your partnership's goals into specific impact areas using frameworks like the 11 Partnership Impacts and 7 Steps Evaluation. For each impact area, select 2–4 measurable indicators. These might include shifts in partner satisfaction scores, the number of shared initiatives launched, or progress in outcome metrics like reduced emissions or improved service access.
Define clear boundaries for the evaluation by specifying the time frame (e.g., 12 months), geographic focus (such as U.S. regions), and the partners and activities that will be assessed. Choose methods and metrics that align with the type of data you collect. For instance, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is ideal for evaluating relationship quality, while Social Network Analysis works well for mapping information flows and network structures. Ensure that the tool you choose supports your data formats - whether surveys, interviews, financial records, or ESG metrics - and that its outputs, such as scores or network diagrams, are easy for leadership to understand and act upon.
Embedding Tools in Decision-Making
To maximize impact, align assessment cycles with existing processes like annual strategy reviews, budget planning, or performance management meetings. This ensures that partnership metrics are reviewed alongside financial and operational data. Incorporate these indicators into performance dashboards or ESG reports so leadership can regularly monitor partnership health, rather than addressing it only during annual reviews. Regular governance meetings can also include partnership "check-ups", providing a structured opportunity to discuss strengths, gaps, and action steps.
Set clear thresholds that trigger reviews and link findings to specific decisions. For assessments involving input from multiple partners, use visual summaries like radar charts or traffic-light scoring systems during facilitated sessions to identify discrepancies in ratings and explore the reasons behind them. Present results as opportunities for growth rather than criticism, and collaborate with partners to create action plans targeting areas like data sharing, joint planning, or funding stability.
Embedding these tools into decision-making routines ensures they drive meaningful improvements.
Applying Tools Repeatedly for Improvement
Establish a regular assessment schedule, whether annually or tied to key project milestones. Each cycle should follow a consistent process: reconfirm impact areas, update methods and metrics if necessary, collect and analyze data, interpret findings, adapt strategies, and re-evaluate. While maintaining a core set of indicators - such as overall partnership synergy, financial impact, and community outcomes - consider adding or retiring metrics as the partnership evolves.
Document how previous assessments have led to tangible changes, such as updates to governance structures, improved communication practices, or revised cost-sharing models. Evaluate whether these changes have resulted in better outcomes. Use concise dashboards that combine numeric scores, color-coded indicators (e.g., red/amber/green thresholds), and brief narrative summaries to make results accessible and actionable for executives and funders. For audiences focused on financial and ESG outcomes, include quantified impacts like cost savings in dollars, revenue growth, or measurable social and environmental benefits, alongside qualitative insights from partners.
How Council Fire Supports Partnership Impact Assessment

Council Fire uses its expertise in sustainability to transform partnership evaluations into strategic tools for success. Serving governments, nonprofits, foundations, and private companies, they create assessment systems that connect partnership performance directly to measurable environmental, social, and financial outcomes.
Aligning Tools with Organizational Goals
Council Fire tailors its assessment frameworks to align with an organization’s strategy, ESG commitments, and partnership objectives. By mapping these elements to a clear theory of change, they help organizations turn broad priorities - like reducing watershed pollution or boosting community resilience - into concrete, measurable outputs and outcomes. For example, if a company aims to cut nutrient loads in a regional watershed, Council Fire develops dashboards that show how each partnership contributes to this goal. These dashboards integrate enterprise KPIs and ESG frameworks, ensuring performance metrics align with both financial and environmental benchmarks.
This alignment not only provides clarity but also lays the groundwork for stronger stakeholder collaboration and customized solutions.
Engaging Stakeholders for Comprehensive Analysis
A successful assessment requires perspectives from all key players - executives, program managers, community groups, and technical experts. Council Fire facilitates this process through workshops, surveys, and structured interviews, gathering honest feedback on partnerships. They adapt self-assessment tools to let stakeholders rate aspects like communication, decision-making, and value creation on clear scales. These responses are then aggregated to uncover areas of agreement and potential conflict.
Additionally, Council Fire employs social network analysis (SNA) to map information flow within partnerships. SNA helps identify weaknesses, bottlenecks, and opportunities to strengthen connections. By combining these insights with qualitative feedback, they provide actionable recommendations to improve governance, streamline operations, and enhance resource allocation.
This comprehensive approach ensures that stakeholder input directly informs the design of actionable solutions.
Crafting Tailored Solutions
When off-the-shelf tools fall short, Council Fire develops custom solutions that blend impact models, self-assessments, and outcome tracking. For instance, they might create a scoring framework that balances factors like climate resilience, equity outcomes, regulatory compliance, and financial performance. These tools often include automated features, such as color-coded thresholds, to make performance levels easy to interpret. Council Fire also trains internal teams to use these tools effectively, ensuring they remain scalable as partnership portfolios grow.
Their approach includes structured annual reviews and midyear check-ins, creating a feedback loop that allows partnerships to adapt to evolving goals. This process refines partnership roles, sharpens focus, and directs investments where they can have the greatest impact.
Conclusion
Choose impact tools that align with your partnership's purpose and development stage, while also considering budget constraints, staff capacity, and ESG requirements. The best strategies blend quantitative methods with qualitative insights. For instance, models like the 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation can work hand-in-hand with tools such as self-assessment questionnaires and social network analysis to evaluate measurable outcomes alongside relationship dynamics.
Data-driven collaboration transforms vague commitments into tangible progress across environmental, social, and financial goals. By analyzing diverse data types - process metrics (e.g., synergy scores and trust levels), network data (e.g., connectivity and information flow), outcome indicators (e.g., community health metrics and environmental improvements), and financial data (e.g., cost savings and return on collaboration) - partners gain a clear, evidence-based foundation for decision-making, moving beyond assumptions.
Incorporating assessments into regular management routines ensures that data informs funding priorities and strategic decisions. Conducting thorough evaluations annually, supplemented by shorter reviews every six to twelve months, allows partnerships to refine their indicators as they evolve. This continuous process paves the way for tailored expert support.
Expert guidance can accelerate progress by clarifying impact objectives, customizing tools for specific sectors, leading stakeholder workshops, and building internal capacity for assessments. Organizations like Council Fire specialize in connecting financial performance with environmental and social outcomes, enabling partners to tie their metrics directly to sustainable, long-term success.
Following an assessment, convene a workshop with key stakeholders to identify three to five actionable improvements. Assign responsibilities, set clear deadlines, update dashboards, and share results with funders. This ongoing cycle of evaluation and refinement strengthens strategic sustainability efforts and drives meaningful, lasting impact.
FAQs
What’s the best way to select a partnership impact assessment tool for my organization?
Choosing a partnership impact assessment tool begins with a clear understanding of your organization’s goals and the specific outcomes you aim to evaluate. Key considerations include how well the tool fits your industry, its user-friendliness, the types of data it requires, and its compatibility with your existing systems.
It’s also important to focus on the kind of insights you need to inform impactful decisions. Seeking advice from professionals, like the experts at Council Fire, can be incredibly helpful in ensuring the tool aligns with your sustainability and impact goals, particularly when adhering to U.S. standards and metrics.
What are the main stages of evaluating a partnership, and which tools are most effective for each?
When assessing a partnership, the process generally unfolds in three key phases:
Setting Objectives and Assessing Impact: This involves clarifying goals and using tools such as impact metrics and stakeholder analysis. These help ensure that all parties are aligned and that potential outcomes are carefully evaluated.
Strategic Planning and Execution: Here, decision-making frameworks and systems thinking come into play. These approaches guide resource allocation and help outline a clear, actionable roadmap for achieving shared objectives.
Ongoing Evaluation and Adjustment: Impact measurement tools are crucial in this stage. They allow for tracking progress, sharing insights, and making necessary adjustments to strategies to stay responsive to changing circumstances.
By following these steps, partnerships can achieve results that are both measurable and meaningful, while remaining flexible to meet new challenges or opportunities.
How can partnership impact assessments support ESG and sustainability goals?
To align partnership impact assessments with ESG and sustainability goals, it's essential to establish clear, measurable metrics that represent your environmental, social, and governance priorities. These metrics should account for both immediate results and long-term effects, such as fostering resilience and supporting ecosystem health.
Involve stakeholders at every stage to ensure the assessment mirrors shared values and promotes collaboration. The insights gained can guide strategic decisions, monitor progress, and uphold accountability. Adding storytelling to the mix can help convey achievements effectively and inspire continued dedication to sustainability objectives.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Dec 19, 2025
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
ESG Strategy
In This Article
Select partnership impact tools—self-assessments, SNA, and evaluation models—to measure collaboration quality, ESG alignment, and financial & community outcomes.
Ultimate Guide to Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Partnership impact assessment tools help organizations evaluate collaboration quality and outcomes, going beyond basic metrics like financial results. These tools are particularly useful for U.S.-based nonprofits, public agencies, businesses, and other groups aiming to meet ESG goals or demonstrate measurable results to stakeholders. Key areas of focus include trust, communication, decision-making, and impacts like cost savings, emissions reductions, or community health improvements.
Key Takeaways:
Purpose: Assess both the process and results of partnerships, including social, environmental, and economic impacts.
Tool Selection: Match tools to your partnership's goals and stage (e.g., start-up, scaling, or renewal).
Implementation: Choose tools that fit your team's capacity and budget, and align with existing frameworks like ESG metrics.
Examples: Use models like the Partnership Impact Model™ for structured evaluations, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool for internal dynamics, or Social Network Analysis (SNA) for mapping relationships.
By integrating these tools into regular management practices, organizations can make better decisions, improve collaboration, and achieve measurable outcomes.

How to Select and Implement Partnership Impact Assessment Tools: A Step-by-Step Guide
Evaluation of Partnerships for Scaling

How to Select Partnership Impact Assessment Tools
Before diving into tool selection, take a moment to clarify your primary goal. Are you performing a "health check" on your partnership, building a business case with ROI metrics, assessing systemic impact, or meeting ESG compliance requirements? Narrow down your options by eliminating tools that don’t align with your specific objective. Once you’ve identified potential tools, focus on three key factors: how well the tool matches your partnership type and lifecycle stage, your team’s capacity to use it effectively, and its compatibility with your current measurement frameworks.
Matching Tools to Partnership Goals and Stages
Partnerships naturally progress through different phases - design, implementation, scaling, or renewal - and each stage has unique measurement needs. The Partnership Impact Model™ can help you align these needs with appropriate tools. For example:
Start-up phase: Rapid assessment tools based on the six Partnership Principles can confirm foundational elements like governance structures and shared expectations.
Implementation phase: Tools such as the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool, which includes 67 questions across 11 themes, are ideal for monitoring collaboration quality and internal dynamics.
Scaling or systems change phase: Broader frameworks become necessary to measure large-scale impacts.
Renewal or close-out phase: Focus on outcome-based tools paired with financial evaluations to assess partner performance against set criteria.
A decision matrix that connects your goals - such as improving coordination, demonstrating community outcomes, or justifying investments - with available tools can simplify the selection process. This approach helps avoid over-measuring by identifying one or two complementary tools.
Implementation Requirements and Growth Capacity
Practical considerations play a critical role in determining a tool’s effectiveness. Short, straightforward instruments - like quick health-check questionnaires - are more likely to be completed by busy partners than lengthy surveys with 60+ questions. Tools using online platforms or simple spreadsheets are faster to deploy compared to those requiring specialized software. To minimize training time and errors, prioritize tools that come with clear user guides and scoring instructions.
When budgeting, calculate the required staff hours, consulting fees, and other costs in U.S. dollars to ensure the tool fits your financial constraints. For partnerships expecting to grow, look for modular tools or those with configurable criteria that can adapt to different organizational levels and partnership sizes. Some tools are specifically designed to identify areas of conflict and consensus among diverse participants, making them valuable in various contexts. Customizable tools can also be adjusted as partnerships evolve, and frameworks that categorize impacts into foundational, operational, and outcome areas can support both initial assessments and more advanced evaluations over time. Importantly, ensure the tool can scale with increasing data volumes without requiring major technological upgrades.
Compatibility with ESG and Sustainability Metrics
To fully evaluate a partnership’s impact, it’s essential to align your tools with existing ESG frameworks. These frameworks provide the structure for indicators and reporting, which is particularly important for organizations issuing sustainability reports or responding to investor inquiries. Tools rooted in multi-dimensional impact models - covering governance, operations, and outcomes - make it easier to connect partnership metrics to ESG categories.
Start by using partnership impact guides to identify and prioritize key impacts, then create specific indicators and metrics that align with ESG requirements. Choose tools that capture both qualitative and quantitative data, ensuring that the evidence gathered can be repurposed for ESG disclosures. For U.S.-based organizations, confirm that metrics can be expressed in commonly used units, such as metric tons of CO₂, gallons of water saved, or jobs created, and that they align with relevant U.S. regulatory or voluntary reporting standards. This alignment ensures your partnership assessments contribute meaningfully to your broader ESG and sustainability goals.
Partnership Impact Tools and Frameworks
When assessing partnerships, it's essential to identify your specific evaluation needs and select the right tools. Three primary options include structured evaluation models, self-assessment questionnaires, and network mapping methods. Each serves a unique purpose: evaluation models focus on tracking outcomes, self-assessment tools evaluate internal collaboration, and network mapping visualizes how individuals and organizations interact. These approaches build on earlier concepts, helping you choose the method that suits your partnership's dynamics.
Partnership Impact Evaluation Models
The 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation, part of the Partnership Impact Model™, offers a flexible framework for use throughout a partnership’s lifecycle. This process involves several stages: conceptualizing impacts, defining and prioritizing them with the Partnership Impact Roadmap, selecting methods and metrics (typically 2–4 indicators per impact), collecting and analyzing data, interpreting results, refining strategies, and evaluating outcomes. The model organizes results into three categories: foundational, operational, and outcome dimensions.
For example, a watershed partnership in the U.S. might begin by conceptualizing impacts like improved water quality, greater community involvement, and cost savings (measured in U.S. dollars). Over the next 12–24 months, they could prioritize specific indicators such as miles of stream restored, shifts in community satisfaction scores, or reductions in annual operating costs. Data collection might involve environmental monitoring and surveys, with results analyzed collaboratively to fine-tune strategies.[1][2]
While structured models offer a systematic approach, self-assessment tools provide valuable insights into the partnership’s internal workings.
Partnership Self-Assessment Tool

The Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is a detailed 67-question survey that evaluates partnership synergy - the added value generated when partners collaborate effectively.[3] Created by the Center for the Advancement of Collaborative Strategies in Health, the tool examines 11 key themes, including leadership, decision-making, resource contributions, and external factors. Respondents rate items using scales like "poor to excellent" or "none of the time to all of the time."
To use this tool, start by selecting the internal partnership to evaluate and identify participants, such as board members, managers, and frontline staff. The survey can be distributed electronically or on paper, with a 2–3 week completion window. Once responses are collected, scores are aggregated by theme to create profiles that reveal strengths and areas needing improvement. Teams can then hold discussions to interpret the results and set clear action plans with timelines and accountability. Conducting the assessment annually or at key milestones helps monitor progress and address issues early.[3]
Social Network Analysis (SNA)
Social Network Analysis (SNA) examines the relationships and interaction patterns within a partnership by using survey data and visualization tools.[1] This method measures attributes such as contact frequency, interaction types (e.g., information sharing or joint planning), trust levels, and the perceived value of relationships. Metrics like network density (overall connectivity), centrality (most influential members), and reciprocity (balance of two-way ties) provide valuable insights. It can also identify structural gaps, such as partners who may be under-connected.
To conduct an SNA, first define the network’s boundaries by deciding which individuals or organizations to include and what types of relationships to measure. A roster-based survey ensures comprehensive data collection, capturing details like contact frequency (daily, weekly, or monthly), trust levels, and the importance of ties. Allow 2–4 weeks for responses, with reminders to encourage participation. Use network mapping software to create visual representations where nodes symbolize organizations and lines represent relationships. Additional visual elements, such as color or size, can highlight factors like role, sector, or influence. These visualizations can then be reviewed in facilitated sessions to guide decisions about governance, equity, and resource allocation. For instance, the analysis might reveal over-reliance on a few central organizations or identify isolated partners who need greater engagement.[1]
Implementing Partnership Assessment Tools
To effectively implement partnership assessment tools, start by clarifying the purpose of your evaluation. Are you justifying funding, improving performance, or considering renewal? Pinpoint your partnership's current lifecycle stage - whether it's in the start-up phase, experiencing growth, well-established, or nearing its conclusion - as the tools and metrics you use will vary depending on this stage. Identify who will use the results, such as internal leaders, partner organizations, community representatives, or funders, and determine how the findings will guide decisions. For example, they might inform adjustments to governance structures or changes to cost-sharing models.
Taking these steps ensures that the assessment directly supports strategic decision-making.
Setting Evaluation Parameters
Translate your partnership's goals into specific impact areas using frameworks like the 11 Partnership Impacts and 7 Steps Evaluation. For each impact area, select 2–4 measurable indicators. These might include shifts in partner satisfaction scores, the number of shared initiatives launched, or progress in outcome metrics like reduced emissions or improved service access.
Define clear boundaries for the evaluation by specifying the time frame (e.g., 12 months), geographic focus (such as U.S. regions), and the partners and activities that will be assessed. Choose methods and metrics that align with the type of data you collect. For instance, the Partnership Self-Assessment Tool is ideal for evaluating relationship quality, while Social Network Analysis works well for mapping information flows and network structures. Ensure that the tool you choose supports your data formats - whether surveys, interviews, financial records, or ESG metrics - and that its outputs, such as scores or network diagrams, are easy for leadership to understand and act upon.
Embedding Tools in Decision-Making
To maximize impact, align assessment cycles with existing processes like annual strategy reviews, budget planning, or performance management meetings. This ensures that partnership metrics are reviewed alongside financial and operational data. Incorporate these indicators into performance dashboards or ESG reports so leadership can regularly monitor partnership health, rather than addressing it only during annual reviews. Regular governance meetings can also include partnership "check-ups", providing a structured opportunity to discuss strengths, gaps, and action steps.
Set clear thresholds that trigger reviews and link findings to specific decisions. For assessments involving input from multiple partners, use visual summaries like radar charts or traffic-light scoring systems during facilitated sessions to identify discrepancies in ratings and explore the reasons behind them. Present results as opportunities for growth rather than criticism, and collaborate with partners to create action plans targeting areas like data sharing, joint planning, or funding stability.
Embedding these tools into decision-making routines ensures they drive meaningful improvements.
Applying Tools Repeatedly for Improvement
Establish a regular assessment schedule, whether annually or tied to key project milestones. Each cycle should follow a consistent process: reconfirm impact areas, update methods and metrics if necessary, collect and analyze data, interpret findings, adapt strategies, and re-evaluate. While maintaining a core set of indicators - such as overall partnership synergy, financial impact, and community outcomes - consider adding or retiring metrics as the partnership evolves.
Document how previous assessments have led to tangible changes, such as updates to governance structures, improved communication practices, or revised cost-sharing models. Evaluate whether these changes have resulted in better outcomes. Use concise dashboards that combine numeric scores, color-coded indicators (e.g., red/amber/green thresholds), and brief narrative summaries to make results accessible and actionable for executives and funders. For audiences focused on financial and ESG outcomes, include quantified impacts like cost savings in dollars, revenue growth, or measurable social and environmental benefits, alongside qualitative insights from partners.
How Council Fire Supports Partnership Impact Assessment

Council Fire uses its expertise in sustainability to transform partnership evaluations into strategic tools for success. Serving governments, nonprofits, foundations, and private companies, they create assessment systems that connect partnership performance directly to measurable environmental, social, and financial outcomes.
Aligning Tools with Organizational Goals
Council Fire tailors its assessment frameworks to align with an organization’s strategy, ESG commitments, and partnership objectives. By mapping these elements to a clear theory of change, they help organizations turn broad priorities - like reducing watershed pollution or boosting community resilience - into concrete, measurable outputs and outcomes. For example, if a company aims to cut nutrient loads in a regional watershed, Council Fire develops dashboards that show how each partnership contributes to this goal. These dashboards integrate enterprise KPIs and ESG frameworks, ensuring performance metrics align with both financial and environmental benchmarks.
This alignment not only provides clarity but also lays the groundwork for stronger stakeholder collaboration and customized solutions.
Engaging Stakeholders for Comprehensive Analysis
A successful assessment requires perspectives from all key players - executives, program managers, community groups, and technical experts. Council Fire facilitates this process through workshops, surveys, and structured interviews, gathering honest feedback on partnerships. They adapt self-assessment tools to let stakeholders rate aspects like communication, decision-making, and value creation on clear scales. These responses are then aggregated to uncover areas of agreement and potential conflict.
Additionally, Council Fire employs social network analysis (SNA) to map information flow within partnerships. SNA helps identify weaknesses, bottlenecks, and opportunities to strengthen connections. By combining these insights with qualitative feedback, they provide actionable recommendations to improve governance, streamline operations, and enhance resource allocation.
This comprehensive approach ensures that stakeholder input directly informs the design of actionable solutions.
Crafting Tailored Solutions
When off-the-shelf tools fall short, Council Fire develops custom solutions that blend impact models, self-assessments, and outcome tracking. For instance, they might create a scoring framework that balances factors like climate resilience, equity outcomes, regulatory compliance, and financial performance. These tools often include automated features, such as color-coded thresholds, to make performance levels easy to interpret. Council Fire also trains internal teams to use these tools effectively, ensuring they remain scalable as partnership portfolios grow.
Their approach includes structured annual reviews and midyear check-ins, creating a feedback loop that allows partnerships to adapt to evolving goals. This process refines partnership roles, sharpens focus, and directs investments where they can have the greatest impact.
Conclusion
Choose impact tools that align with your partnership's purpose and development stage, while also considering budget constraints, staff capacity, and ESG requirements. The best strategies blend quantitative methods with qualitative insights. For instance, models like the 7 Steps of Partnership Impact Evaluation can work hand-in-hand with tools such as self-assessment questionnaires and social network analysis to evaluate measurable outcomes alongside relationship dynamics.
Data-driven collaboration transforms vague commitments into tangible progress across environmental, social, and financial goals. By analyzing diverse data types - process metrics (e.g., synergy scores and trust levels), network data (e.g., connectivity and information flow), outcome indicators (e.g., community health metrics and environmental improvements), and financial data (e.g., cost savings and return on collaboration) - partners gain a clear, evidence-based foundation for decision-making, moving beyond assumptions.
Incorporating assessments into regular management routines ensures that data informs funding priorities and strategic decisions. Conducting thorough evaluations annually, supplemented by shorter reviews every six to twelve months, allows partnerships to refine their indicators as they evolve. This continuous process paves the way for tailored expert support.
Expert guidance can accelerate progress by clarifying impact objectives, customizing tools for specific sectors, leading stakeholder workshops, and building internal capacity for assessments. Organizations like Council Fire specialize in connecting financial performance with environmental and social outcomes, enabling partners to tie their metrics directly to sustainable, long-term success.
Following an assessment, convene a workshop with key stakeholders to identify three to five actionable improvements. Assign responsibilities, set clear deadlines, update dashboards, and share results with funders. This ongoing cycle of evaluation and refinement strengthens strategic sustainability efforts and drives meaningful, lasting impact.
FAQs
What’s the best way to select a partnership impact assessment tool for my organization?
Choosing a partnership impact assessment tool begins with a clear understanding of your organization’s goals and the specific outcomes you aim to evaluate. Key considerations include how well the tool fits your industry, its user-friendliness, the types of data it requires, and its compatibility with your existing systems.
It’s also important to focus on the kind of insights you need to inform impactful decisions. Seeking advice from professionals, like the experts at Council Fire, can be incredibly helpful in ensuring the tool aligns with your sustainability and impact goals, particularly when adhering to U.S. standards and metrics.
What are the main stages of evaluating a partnership, and which tools are most effective for each?
When assessing a partnership, the process generally unfolds in three key phases:
Setting Objectives and Assessing Impact: This involves clarifying goals and using tools such as impact metrics and stakeholder analysis. These help ensure that all parties are aligned and that potential outcomes are carefully evaluated.
Strategic Planning and Execution: Here, decision-making frameworks and systems thinking come into play. These approaches guide resource allocation and help outline a clear, actionable roadmap for achieving shared objectives.
Ongoing Evaluation and Adjustment: Impact measurement tools are crucial in this stage. They allow for tracking progress, sharing insights, and making necessary adjustments to strategies to stay responsive to changing circumstances.
By following these steps, partnerships can achieve results that are both measurable and meaningful, while remaining flexible to meet new challenges or opportunities.
How can partnership impact assessments support ESG and sustainability goals?
To align partnership impact assessments with ESG and sustainability goals, it's essential to establish clear, measurable metrics that represent your environmental, social, and governance priorities. These metrics should account for both immediate results and long-term effects, such as fostering resilience and supporting ecosystem health.
Involve stakeholders at every stage to ensure the assessment mirrors shared values and promotes collaboration. The insights gained can guide strategic decisions, monitor progress, and uphold accountability. Adding storytelling to the mix can help convey achievements effectively and inspire continued dedication to sustainability objectives.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
What makes Council Fire different?
Who does Council Fire you work with?
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


