


Dec 19, 2025
Dec 19, 2025
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Sustainability Strategy
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
Digital tools—dashboards, AI, and participatory platforms—boost transparency, two‑way communication, and cross‑sector collaboration for sustainability, but equity gaps persist.
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping how organizations connect with stakeholders to address sustainability challenges. By integrating digital tools like AI, data platforms, and participatory forums, companies improve transparency, enable two-way communication, and foster collaboration across sectors. Research shows that IT investments enhance engagement and drive measurable improvements in environmental, social, and economic outcomes. However, challenges such as the digital divide and underrepresentation of marginalized groups remain.
Key Takeaways:
Transparency: Real-time dashboards and data platforms build trust by providing accessible information.
Two-Way Communication: Digital tools empower stakeholders to give feedback and influence decisions.
Collaboration: Platforms streamline efforts across governments, NGOs, and businesses.
Challenges: Digital exclusion and a lack of long-term studies hinder progress.
Organizations must align IT investments with sustainability goals, design effective engagement processes, and act on stakeholder insights to achieve meaningful results.
Technology's Impact on Stakeholder Engagement and Sustainability Outcomes
The Importance of Stakeholder Engagement in Sustainability | Yale SOM



Research Overview: Findings and Methods
Exploring how technology influences stakeholder engagement in sustainability efforts involves a wide range of approaches and organizational settings. Studies have looked at the practices of multinational corporations, local governments, and nonprofits in managing various sustainability initiatives. These include large-scale projects in construction and energy sectors, where digital tools improve efficiency, as well as community-focused efforts that bring together companies, NGOs, and local authorities. Below, we break down the primary study categories, research methods, and key areas where further work is needed.
Study Categories
Researchers have taken different approaches to analyze the role of technology in sustainability:
Quantitative Models: These studies rely on survey data from industries like engineering, construction, and corporate management to explore the links between IT investments, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability outcomes.
Qualitative Case Studies: These focus on the dynamics of collaboration during sustainability transformations, shedding light on issues like power imbalances and challenges in creating inclusive processes.
Applied Evaluations: These examine the practical use of digital tools, such as social media for public consultations, data platforms for monitoring emissions, and collaborative software for coordinating efforts across sectors.
Research Methods Used
The methods employed in these studies are as varied as the questions they aim to answer:
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM): This statistical technique has been particularly effective in assessing the impact of IT investments on sustainability, with findings showing significant correlations [3].
Systematic Literature Reviews: These synthesize existing research on topics like "Digital CSR" and "Green IT", helping to establish theoretical foundations for how technology can enhance engagement.
Qualitative Approaches: Methods such as detailed case studies, participatory research involving stakeholders, and comparative analyses using frameworks like the five-pillar method (focusing on agency, system roles, power dynamics, problem alignment, and potential for transformation) provide deeper insights into the nuances of technology-enabled engagement.
While these methods have yielded valuable findings, there are still critical gaps in the research that need to be addressed.
Research Gaps
Despite the progress made, several limitations persist in this field of study:
Geographic Focus: Much of the existing research is centered on Western contexts, with limited attention to non-OECD regions and the Global South. This lack of diversity leaves out important perspectives and experiences.
Longitudinal Studies: Few studies examine the long-term effects of technology-enabled engagement, making it difficult to evaluate sustained outcomes over time.
Marginalized Stakeholders: Vulnerable and underrepresented groups are often overlooked, raising concerns about whether digital tools genuinely empower these communities or inadvertently exclude them.
Future research should address these gaps by exploring who benefits most from technology-driven engagement, particularly in contexts with significant power disparities. Doing so will help refine strategies for digital engagement and ensure more equitable and effective sustainability outcomes.
How Technology Changes Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping the way organizations engage with stakeholders in sustainability efforts. Gone are the days of relying solely on periodic reports or one-off public meetings. Today, digital platforms enable ongoing interaction, turning stakeholders into active participants. These tools allow stakeholders to monitor progress, provide feedback, and collaborate on solutions in real time. This shift is driving three key changes: greater transparency through accessible data, more dynamic two-way communication, and stronger cross-sector collaboration. Let’s explore how these changes are transforming stakeholder engagement.
Transparency and Information Access
Digital platforms are making transparency a cornerstone of stakeholder engagement. By offering direct access to sustainability data, these tools empower stakeholders to verify information themselves. Centralized dashboards and monitoring systems allow communities, investors, and regulators to track key metrics - like emissions, resource consumption, and project milestones - in real time. For instance, emissions tracking software and supply chain analysis tools provide a clear picture of environmental impact in relation to operational targets, building trust through verifiable data [4]. Organizations using real-time dashboards often report increased stakeholder confidence, especially when the data spans entire supply chains and highlights consistent progress toward sustainability goals.
Two-Way Communication
Digital tools like social media platforms, online consultations, and participatory forums are revolutionizing communication between organizations and stakeholders. Instead of one-way updates, companies can now engage in meaningful dialogue, gathering input and feedback from diverse groups. This approach not only keeps stakeholders informed but also empowers them to influence project decisions [2]. Platforms that facilitate participatory decision-making and stakeholder forums help integrate various perspectives, leading to policies that are more context-aware and widely supported. Research shows that strong stakeholder engagement, supported by effective two-way communication, improves sustainability outcomes and overall project performance [3]. By enabling continuous interaction, digital tools ensure stakeholders remain involved throughout a project’s lifecycle, rather than only at select stages.
Cross-Sector Collaboration
Digital platforms are also breaking down barriers between sectors, fostering collaboration among governments, NGOs, private companies, and local communities. These tools facilitate joint problem-solving and resource sharing through features like document sharing, real-time project tracking, and coordinated planning. This interconnected approach leverages collective expertise and resources, driving innovation and improving project outcomes [3][6].
The rise of cross-sector collaboration reflects a broader trend toward multi-stakeholder governance in sustainability initiatives. Networks that link customers, NGOs, and governments play a critical role in driving sustainability transitions. Policies from organizations like the Green Climate Fund now mandate the use of digital tools to ensure inclusive engagement [2]. Companies like Council Fire are helping organizations design and implement digital strategies that align financial, environmental, and social objectives. By integrating IT systems with stakeholder engagement, they’re enabling coordinated action across sectors in areas like energy, water, transportation, and sustainable community development.
Technology's Effect on Sustainability Results
The integration of digital tools into sustainability efforts is proving to be a game-changer, delivering measurable improvements across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research highlights that combining IT investments with stakeholder engagement leads to tangible progress, showing technology's critical role in driving sustainability outcomes [3][5]. Organizations that align their digital strategies with sustainability goals are reaping rewards such as lower emissions, stronger community relationships, and improved project performance. Let’s delve into the specific impacts on each dimension.
Environmental Results
Digital technologies are transforming environmental efforts by enabling real-time monitoring and more informed decision-making. For instance, AI-powered dashboards that track supply chain impacts allow businesses to identify and act on reduction opportunities, maximizing resource use while minimizing their environmental footprint [3][4]. Policies from groups like the Green Climate Fund now emphasize the use of tech-enabled consultations, combining local expertise with data insights to enhance emissions reduction and resource management efforts [2][4].
Virtual consultations, for example, cut down on travel-related emissions, while GIS mapping tools help stakeholders pinpoint areas for conservation and biodiversity protection. By giving stakeholders access to environmental data, these tools empower them to challenge outdated assumptions and spark green innovations that might otherwise go unnoticed [2][4].
Social Results
Technology is also reshaping social outcomes by expanding participation and fostering trust. Digital platforms, such as mobile-friendly tools and asynchronous forums, make it easier for people with non-traditional schedules, caregiving responsibilities, or mobility challenges to engage. Tools like GIS and data overlays further assist organizations in identifying underserved communities, ensuring equitable distribution of resources like green spaces and clean energy infrastructure.
By enhancing transparency, digital tools build trust through "closed-loop" communication, allowing stakeholders to see how their input influences decisions. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge. Economic inequalities and power imbalances can exclude marginalized groups from participating meaningfully. To address this, hybrid approaches that combine digital tools with traditional outreach methods are essential to ensure inclusive and authentic engagement [2][6].
Economic Results
Investments in IT are proving to be cost-effective while driving better project outcomes [3][5]. Digital platforms reduce the need for costly in-person meetings and manual processes by automating data collection and enabling virtual collaboration. They also help organizations detect stakeholder concerns early through sentiment analysis and real-time monitoring, minimizing risks like project delays, legal disputes, or community pushback.
When technology is strategically aligned with environmental and social goals, it becomes more than just a cost-saving tool - it becomes a competitive advantage. Studies applying the resource-based view show that organizations treating sustainability-focused IT - like monitoring systems and collaboration platforms - as strategic assets achieve stronger project results [3]. Stakeholder feedback gathered through these tools fosters resource efficiency and innovation, enhancing risk management and supporting overall success through collaborative engagement.
What Organizations Should Do
Research underscores a clear message: technology can deliver meaningful sustainability outcomes when it aligns with stakeholder engagement and environmental objectives. To achieve this, organizations must treat IT investments as tools for sustainability, create engagement processes that empower stakeholders, and turn insights into actionable projects. Here’s how they can make it happen:
Aligning IT Investments with Sustainability Goals
The first step is to identify the specific sustainability challenges and stakeholder needs before selecting the right technology. Too often, organizations jump straight to purchasing tools - such as dashboards or platforms - without fully understanding the problems they aim to solve or the people they intend to serve. When IT capabilities are directly tied to sustainability objectives, they evolve into strategic tools that can provide a competitive edge.
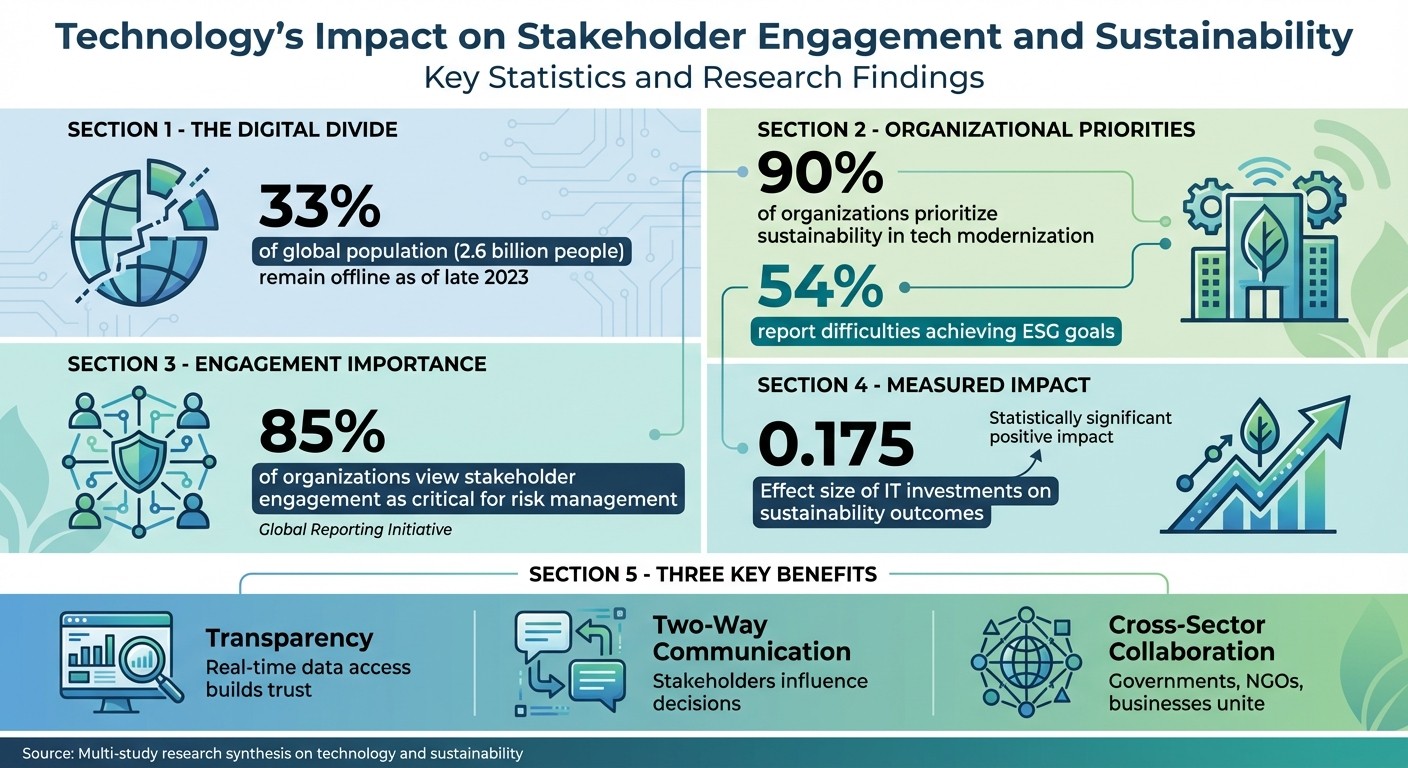
For example, integrated data systems that merge environmental, social, and economic performance into a single, comprehensive source of truth can be a game changer. Tools like emissions tracking software, which links supply chain data to business priorities, can transform vague climate commitments into actionable strategies [4]. These systems not only build stakeholder trust but also help meet reporting requirements. Still, despite 90% of organizations prioritizing sustainability in their tech modernization efforts, 54% report difficulties in achieving their ESG goals [4].
Specialized guidance from partners like Council Fire can also be invaluable. They assist organizations in merging financial performance with environmental and social outcomes through a mix of strategic advice and stakeholder collaboration. Their expertise can help pinpoint the most effective technology investments for areas like natural resource management, climate resilience, and sustainable infrastructure. Once the right tools are in place, organizations need to ensure that these investments are supported by effective engagement processes.
Designing Meaningful Engagement Processes
Engagement that feels tokenistic - where feedback is collected but doesn’t influence decisions - can erode trust. To prevent this, it’s important to define from the start which decisions will be shaped by stakeholder input and communicate those parameters clearly [2][6][7]. Structured stakeholder analysis can help identify who holds influence, agency, and alignment with the relevant issues, ensuring that digital tools like surveys, virtual workshops, participatory mapping, or mobile apps meet the needs of the people they are meant to serve.
According to the Global Reporting Initiative, 85% of organizations view stakeholder engagement as critical for effective risk management [2]. However, meaningful engagement requires more than just surveys. Organizations should implement "closed-loop" communication, showing stakeholders how their feedback has shaped project decisions. This could involve updates via online platforms or dashboards. Additionally, it’s important to address the digital divide by combining online and traditional outreach methods, such as phone calls, in-person meetings, or printed materials, to ensure that marginalized groups aren’t left out due to connectivity issues or low digital literacy.
Strong governance is essential to these efforts. Cross-functional teams - comprising representatives from sustainability, IT, operations, and communications - should oversee technology decisions, establish data standards, and ensure the quality of engagement efforts [4]. Clearly defining roles for managing stakeholder strategies, platforms, and ESG data is key, as is training staff to interpret sustainability analytics, facilitate online discussions, and translate complex data into easy-to-understand narratives [4][6]. With a solid engagement framework in place, organizations can focus on applying these insights to real-world projects.
Turning Insights into Actionable Projects
With IT aligned to sustainability goals and robust engagement strategies in place, organizations can use tools like GIS mapping and climate risk platforms in resilience planning. These technologies allow them to visualize hazards such as flooding or extreme heat, while inviting community input through interactive maps and virtual workshops [6][7]. For instance, creating portals where residents can submit resilience ideas, rank priorities, and track funding decisions can directly connect IT investments - like early warning systems or sensor networks - to the vulnerabilities identified by stakeholders.
A practical example of this approach comes from August 2016, when the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council, supported by Council Fire, used a stakeholder-driven risk assessment framework to apply ecosystem research to fisheries management. Facilitators like George Lapointe worked with stakeholders to identify and rank 12 key ecosystem elements. This collaboration led to the adoption of the Ecosystem Approach to Fisheries Management Guidance Document, which now governs 14 species by addressing high-risk interactions such as climate change and habitat loss.
In community development, studies show that IT investments can positively influence sustainability outcomes (effect size 0.175) [3]. By incorporating digital tools for participatory decision-making - such as real-time dashboards - organizations can empower employees and community members to better understand and improve their environmental and social impact. Piloting these technologies on a small scale, evaluating their effectiveness, and scaling up successful solutions can help bridge the gap between research and practical application.
Conclusion
Technology now plays a pivotal role in driving effective stakeholder engagement and advancing sustainability efforts. When organizations strategically align their IT investments with sustainability goals, they can achieve measurable benefits across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research underscores this connection, showing a statistically significant positive impact of IT investments on sustainability outcomes, reinforcing the notion that technology is indispensable for embedding sustainable practices into projects [3]. Additionally, stakeholder engagement has been shown to enhance sustainability performance, which subsequently improves overall project success [3]. However, challenges such as digital exclusion and inequities in participation remain significant barriers to fully realizing these benefits.
Despite technological advancements, a substantial digital divide persists. As of late 2023, about 33% of the global population - roughly 2.6 billion people - remained offline [1]. This stark reality highlights the limitations of digital-only strategies and underscores the importance of blending online tools with offline engagement methods. To address these gaps, organizations must adopt stakeholder analysis frameworks that consider power dynamics, ensuring that feedback mechanisms are meaningful and not merely procedural.
Future research must also address critical gaps in understanding. While existing studies affirm the link between IT, engagement, and sustainability, there is a lack of long-term analyses on digital engagement [6]. Equity-focused research and comparative studies across technologies, regions, and stakeholder groups will be essential for refining these insights and guiding future strategies.
For U.S. organizations, the urgency to align IT with sustainability is heightened by increasing regulatory demands, investor expectations, and community pressure regarding ESG and climate disclosures [4]. Council Fire exemplifies how organizations can integrate financial, environmental, and social performance through targeted strategies and stakeholder collaboration. By offering actionable roadmaps for sectors such as natural resource management, energy and water infrastructure, and sustainable communities, Council Fire demonstrates how expert guidance can translate research into impactful sustainability initiatives.
As technology continues to shape how organizations balance sustainability trade-offs, success will depend on strong governance, inclusive design, and a commitment to continuous improvement [4]. Moving forward, organizations must treat technology, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability as interconnected priorities. By investing in inclusive practices and fostering accountability, they can better navigate the complex challenges of sustainability and build trust with stakeholders [3]. Those that adopt this integrated approach will be well-equipped to tackle the pressing sustainability demands of the future.
FAQs
What can organizations do to bridge the digital divide in stakeholder engagement?
To address the digital divide in stakeholder engagement, organizations should prioritize inclusive communication by leveraging a mix of digital platforms tailored to reach diverse groups. Offering digital literacy training equips stakeholders with the skills to engage effectively, while ensuring affordable and dependable access to technology and internet connectivity promotes fair opportunities for participation. These efforts can lead to stronger collaboration and deeper connections with stakeholders.
How does aligning IT investments with sustainability goals benefit organizations?
Aligning IT investments with sustainability objectives allows organizations to establish deeper connections with stakeholders through openness, informed decision-making, and enhanced teamwork. These initiatives strengthen trust, improve communication, and lay the groundwork for lasting resilience and mutual growth.
Incorporating sustainability into IT strategies enables organizations to tackle environmental and social challenges more effectively while delivering measurable results that reflect their values and support their business goals.
How do digital tools improve communication and collaboration with stakeholders?
Digital tools have transformed the way organizations communicate and collaborate with their stakeholders, making interactions more immediate, open, and easy to access. With platforms like social media, video conferencing, and other collaborative tools, real-time discussions are now possible, which helps build trust and encourages active involvement.
These technologies simplify the feedback process, ensure updates are shared quickly, and open the door for deeper, more meaningful engagement. This ultimately leads to stronger and more effective connections with stakeholders.
Related Blog Posts

Latest Articles
©2025
FAQ
FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Dec 19, 2025
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
Digital tools—dashboards, AI, and participatory platforms—boost transparency, two‑way communication, and cross‑sector collaboration for sustainability, but equity gaps persist.
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping how organizations connect with stakeholders to address sustainability challenges. By integrating digital tools like AI, data platforms, and participatory forums, companies improve transparency, enable two-way communication, and foster collaboration across sectors. Research shows that IT investments enhance engagement and drive measurable improvements in environmental, social, and economic outcomes. However, challenges such as the digital divide and underrepresentation of marginalized groups remain.
Key Takeaways:
Transparency: Real-time dashboards and data platforms build trust by providing accessible information.
Two-Way Communication: Digital tools empower stakeholders to give feedback and influence decisions.
Collaboration: Platforms streamline efforts across governments, NGOs, and businesses.
Challenges: Digital exclusion and a lack of long-term studies hinder progress.
Organizations must align IT investments with sustainability goals, design effective engagement processes, and act on stakeholder insights to achieve meaningful results.

Technology's Impact on Stakeholder Engagement and Sustainability Outcomes
The Importance of Stakeholder Engagement in Sustainability | Yale SOM


Research Overview: Findings and Methods
Exploring how technology influences stakeholder engagement in sustainability efforts involves a wide range of approaches and organizational settings. Studies have looked at the practices of multinational corporations, local governments, and nonprofits in managing various sustainability initiatives. These include large-scale projects in construction and energy sectors, where digital tools improve efficiency, as well as community-focused efforts that bring together companies, NGOs, and local authorities. Below, we break down the primary study categories, research methods, and key areas where further work is needed.
Study Categories
Researchers have taken different approaches to analyze the role of technology in sustainability:
Quantitative Models: These studies rely on survey data from industries like engineering, construction, and corporate management to explore the links between IT investments, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability outcomes.
Qualitative Case Studies: These focus on the dynamics of collaboration during sustainability transformations, shedding light on issues like power imbalances and challenges in creating inclusive processes.
Applied Evaluations: These examine the practical use of digital tools, such as social media for public consultations, data platforms for monitoring emissions, and collaborative software for coordinating efforts across sectors.
Research Methods Used
The methods employed in these studies are as varied as the questions they aim to answer:
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM): This statistical technique has been particularly effective in assessing the impact of IT investments on sustainability, with findings showing significant correlations [3].
Systematic Literature Reviews: These synthesize existing research on topics like "Digital CSR" and "Green IT", helping to establish theoretical foundations for how technology can enhance engagement.
Qualitative Approaches: Methods such as detailed case studies, participatory research involving stakeholders, and comparative analyses using frameworks like the five-pillar method (focusing on agency, system roles, power dynamics, problem alignment, and potential for transformation) provide deeper insights into the nuances of technology-enabled engagement.
While these methods have yielded valuable findings, there are still critical gaps in the research that need to be addressed.
Research Gaps
Despite the progress made, several limitations persist in this field of study:
Geographic Focus: Much of the existing research is centered on Western contexts, with limited attention to non-OECD regions and the Global South. This lack of diversity leaves out important perspectives and experiences.
Longitudinal Studies: Few studies examine the long-term effects of technology-enabled engagement, making it difficult to evaluate sustained outcomes over time.
Marginalized Stakeholders: Vulnerable and underrepresented groups are often overlooked, raising concerns about whether digital tools genuinely empower these communities or inadvertently exclude them.
Future research should address these gaps by exploring who benefits most from technology-driven engagement, particularly in contexts with significant power disparities. Doing so will help refine strategies for digital engagement and ensure more equitable and effective sustainability outcomes.
How Technology Changes Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping the way organizations engage with stakeholders in sustainability efforts. Gone are the days of relying solely on periodic reports or one-off public meetings. Today, digital platforms enable ongoing interaction, turning stakeholders into active participants. These tools allow stakeholders to monitor progress, provide feedback, and collaborate on solutions in real time. This shift is driving three key changes: greater transparency through accessible data, more dynamic two-way communication, and stronger cross-sector collaboration. Let’s explore how these changes are transforming stakeholder engagement.
Transparency and Information Access
Digital platforms are making transparency a cornerstone of stakeholder engagement. By offering direct access to sustainability data, these tools empower stakeholders to verify information themselves. Centralized dashboards and monitoring systems allow communities, investors, and regulators to track key metrics - like emissions, resource consumption, and project milestones - in real time. For instance, emissions tracking software and supply chain analysis tools provide a clear picture of environmental impact in relation to operational targets, building trust through verifiable data [4]. Organizations using real-time dashboards often report increased stakeholder confidence, especially when the data spans entire supply chains and highlights consistent progress toward sustainability goals.
Two-Way Communication
Digital tools like social media platforms, online consultations, and participatory forums are revolutionizing communication between organizations and stakeholders. Instead of one-way updates, companies can now engage in meaningful dialogue, gathering input and feedback from diverse groups. This approach not only keeps stakeholders informed but also empowers them to influence project decisions [2]. Platforms that facilitate participatory decision-making and stakeholder forums help integrate various perspectives, leading to policies that are more context-aware and widely supported. Research shows that strong stakeholder engagement, supported by effective two-way communication, improves sustainability outcomes and overall project performance [3]. By enabling continuous interaction, digital tools ensure stakeholders remain involved throughout a project’s lifecycle, rather than only at select stages.
Cross-Sector Collaboration
Digital platforms are also breaking down barriers between sectors, fostering collaboration among governments, NGOs, private companies, and local communities. These tools facilitate joint problem-solving and resource sharing through features like document sharing, real-time project tracking, and coordinated planning. This interconnected approach leverages collective expertise and resources, driving innovation and improving project outcomes [3][6].
The rise of cross-sector collaboration reflects a broader trend toward multi-stakeholder governance in sustainability initiatives. Networks that link customers, NGOs, and governments play a critical role in driving sustainability transitions. Policies from organizations like the Green Climate Fund now mandate the use of digital tools to ensure inclusive engagement [2]. Companies like Council Fire are helping organizations design and implement digital strategies that align financial, environmental, and social objectives. By integrating IT systems with stakeholder engagement, they’re enabling coordinated action across sectors in areas like energy, water, transportation, and sustainable community development.
Technology's Effect on Sustainability Results
The integration of digital tools into sustainability efforts is proving to be a game-changer, delivering measurable improvements across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research highlights that combining IT investments with stakeholder engagement leads to tangible progress, showing technology's critical role in driving sustainability outcomes [3][5]. Organizations that align their digital strategies with sustainability goals are reaping rewards such as lower emissions, stronger community relationships, and improved project performance. Let’s delve into the specific impacts on each dimension.
Environmental Results
Digital technologies are transforming environmental efforts by enabling real-time monitoring and more informed decision-making. For instance, AI-powered dashboards that track supply chain impacts allow businesses to identify and act on reduction opportunities, maximizing resource use while minimizing their environmental footprint [3][4]. Policies from groups like the Green Climate Fund now emphasize the use of tech-enabled consultations, combining local expertise with data insights to enhance emissions reduction and resource management efforts [2][4].
Virtual consultations, for example, cut down on travel-related emissions, while GIS mapping tools help stakeholders pinpoint areas for conservation and biodiversity protection. By giving stakeholders access to environmental data, these tools empower them to challenge outdated assumptions and spark green innovations that might otherwise go unnoticed [2][4].
Social Results
Technology is also reshaping social outcomes by expanding participation and fostering trust. Digital platforms, such as mobile-friendly tools and asynchronous forums, make it easier for people with non-traditional schedules, caregiving responsibilities, or mobility challenges to engage. Tools like GIS and data overlays further assist organizations in identifying underserved communities, ensuring equitable distribution of resources like green spaces and clean energy infrastructure.
By enhancing transparency, digital tools build trust through "closed-loop" communication, allowing stakeholders to see how their input influences decisions. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge. Economic inequalities and power imbalances can exclude marginalized groups from participating meaningfully. To address this, hybrid approaches that combine digital tools with traditional outreach methods are essential to ensure inclusive and authentic engagement [2][6].
Economic Results
Investments in IT are proving to be cost-effective while driving better project outcomes [3][5]. Digital platforms reduce the need for costly in-person meetings and manual processes by automating data collection and enabling virtual collaboration. They also help organizations detect stakeholder concerns early through sentiment analysis and real-time monitoring, minimizing risks like project delays, legal disputes, or community pushback.
When technology is strategically aligned with environmental and social goals, it becomes more than just a cost-saving tool - it becomes a competitive advantage. Studies applying the resource-based view show that organizations treating sustainability-focused IT - like monitoring systems and collaboration platforms - as strategic assets achieve stronger project results [3]. Stakeholder feedback gathered through these tools fosters resource efficiency and innovation, enhancing risk management and supporting overall success through collaborative engagement.
What Organizations Should Do
Research underscores a clear message: technology can deliver meaningful sustainability outcomes when it aligns with stakeholder engagement and environmental objectives. To achieve this, organizations must treat IT investments as tools for sustainability, create engagement processes that empower stakeholders, and turn insights into actionable projects. Here’s how they can make it happen:
Aligning IT Investments with Sustainability Goals
The first step is to identify the specific sustainability challenges and stakeholder needs before selecting the right technology. Too often, organizations jump straight to purchasing tools - such as dashboards or platforms - without fully understanding the problems they aim to solve or the people they intend to serve. When IT capabilities are directly tied to sustainability objectives, they evolve into strategic tools that can provide a competitive edge.
For example, integrated data systems that merge environmental, social, and economic performance into a single, comprehensive source of truth can be a game changer. Tools like emissions tracking software, which links supply chain data to business priorities, can transform vague climate commitments into actionable strategies [4]. These systems not only build stakeholder trust but also help meet reporting requirements. Still, despite 90% of organizations prioritizing sustainability in their tech modernization efforts, 54% report difficulties in achieving their ESG goals [4].
Specialized guidance from partners like Council Fire can also be invaluable. They assist organizations in merging financial performance with environmental and social outcomes through a mix of strategic advice and stakeholder collaboration. Their expertise can help pinpoint the most effective technology investments for areas like natural resource management, climate resilience, and sustainable infrastructure. Once the right tools are in place, organizations need to ensure that these investments are supported by effective engagement processes.
Designing Meaningful Engagement Processes
Engagement that feels tokenistic - where feedback is collected but doesn’t influence decisions - can erode trust. To prevent this, it’s important to define from the start which decisions will be shaped by stakeholder input and communicate those parameters clearly [2][6][7]. Structured stakeholder analysis can help identify who holds influence, agency, and alignment with the relevant issues, ensuring that digital tools like surveys, virtual workshops, participatory mapping, or mobile apps meet the needs of the people they are meant to serve.
According to the Global Reporting Initiative, 85% of organizations view stakeholder engagement as critical for effective risk management [2]. However, meaningful engagement requires more than just surveys. Organizations should implement "closed-loop" communication, showing stakeholders how their feedback has shaped project decisions. This could involve updates via online platforms or dashboards. Additionally, it’s important to address the digital divide by combining online and traditional outreach methods, such as phone calls, in-person meetings, or printed materials, to ensure that marginalized groups aren’t left out due to connectivity issues or low digital literacy.
Strong governance is essential to these efforts. Cross-functional teams - comprising representatives from sustainability, IT, operations, and communications - should oversee technology decisions, establish data standards, and ensure the quality of engagement efforts [4]. Clearly defining roles for managing stakeholder strategies, platforms, and ESG data is key, as is training staff to interpret sustainability analytics, facilitate online discussions, and translate complex data into easy-to-understand narratives [4][6]. With a solid engagement framework in place, organizations can focus on applying these insights to real-world projects.
Turning Insights into Actionable Projects
With IT aligned to sustainability goals and robust engagement strategies in place, organizations can use tools like GIS mapping and climate risk platforms in resilience planning. These technologies allow them to visualize hazards such as flooding or extreme heat, while inviting community input through interactive maps and virtual workshops [6][7]. For instance, creating portals where residents can submit resilience ideas, rank priorities, and track funding decisions can directly connect IT investments - like early warning systems or sensor networks - to the vulnerabilities identified by stakeholders.
A practical example of this approach comes from August 2016, when the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council, supported by Council Fire, used a stakeholder-driven risk assessment framework to apply ecosystem research to fisheries management. Facilitators like George Lapointe worked with stakeholders to identify and rank 12 key ecosystem elements. This collaboration led to the adoption of the Ecosystem Approach to Fisheries Management Guidance Document, which now governs 14 species by addressing high-risk interactions such as climate change and habitat loss.
In community development, studies show that IT investments can positively influence sustainability outcomes (effect size 0.175) [3]. By incorporating digital tools for participatory decision-making - such as real-time dashboards - organizations can empower employees and community members to better understand and improve their environmental and social impact. Piloting these technologies on a small scale, evaluating their effectiveness, and scaling up successful solutions can help bridge the gap between research and practical application.
Conclusion
Technology now plays a pivotal role in driving effective stakeholder engagement and advancing sustainability efforts. When organizations strategically align their IT investments with sustainability goals, they can achieve measurable benefits across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research underscores this connection, showing a statistically significant positive impact of IT investments on sustainability outcomes, reinforcing the notion that technology is indispensable for embedding sustainable practices into projects [3]. Additionally, stakeholder engagement has been shown to enhance sustainability performance, which subsequently improves overall project success [3]. However, challenges such as digital exclusion and inequities in participation remain significant barriers to fully realizing these benefits.
Despite technological advancements, a substantial digital divide persists. As of late 2023, about 33% of the global population - roughly 2.6 billion people - remained offline [1]. This stark reality highlights the limitations of digital-only strategies and underscores the importance of blending online tools with offline engagement methods. To address these gaps, organizations must adopt stakeholder analysis frameworks that consider power dynamics, ensuring that feedback mechanisms are meaningful and not merely procedural.
Future research must also address critical gaps in understanding. While existing studies affirm the link between IT, engagement, and sustainability, there is a lack of long-term analyses on digital engagement [6]. Equity-focused research and comparative studies across technologies, regions, and stakeholder groups will be essential for refining these insights and guiding future strategies.
For U.S. organizations, the urgency to align IT with sustainability is heightened by increasing regulatory demands, investor expectations, and community pressure regarding ESG and climate disclosures [4]. Council Fire exemplifies how organizations can integrate financial, environmental, and social performance through targeted strategies and stakeholder collaboration. By offering actionable roadmaps for sectors such as natural resource management, energy and water infrastructure, and sustainable communities, Council Fire demonstrates how expert guidance can translate research into impactful sustainability initiatives.
As technology continues to shape how organizations balance sustainability trade-offs, success will depend on strong governance, inclusive design, and a commitment to continuous improvement [4]. Moving forward, organizations must treat technology, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability as interconnected priorities. By investing in inclusive practices and fostering accountability, they can better navigate the complex challenges of sustainability and build trust with stakeholders [3]. Those that adopt this integrated approach will be well-equipped to tackle the pressing sustainability demands of the future.
FAQs
What can organizations do to bridge the digital divide in stakeholder engagement?
To address the digital divide in stakeholder engagement, organizations should prioritize inclusive communication by leveraging a mix of digital platforms tailored to reach diverse groups. Offering digital literacy training equips stakeholders with the skills to engage effectively, while ensuring affordable and dependable access to technology and internet connectivity promotes fair opportunities for participation. These efforts can lead to stronger collaboration and deeper connections with stakeholders.
How does aligning IT investments with sustainability goals benefit organizations?
Aligning IT investments with sustainability objectives allows organizations to establish deeper connections with stakeholders through openness, informed decision-making, and enhanced teamwork. These initiatives strengthen trust, improve communication, and lay the groundwork for lasting resilience and mutual growth.
Incorporating sustainability into IT strategies enables organizations to tackle environmental and social challenges more effectively while delivering measurable results that reflect their values and support their business goals.
How do digital tools improve communication and collaboration with stakeholders?
Digital tools have transformed the way organizations communicate and collaborate with their stakeholders, making interactions more immediate, open, and easy to access. With platforms like social media, video conferencing, and other collaborative tools, real-time discussions are now possible, which helps build trust and encourages active involvement.
These technologies simplify the feedback process, ensure updates are shared quickly, and open the door for deeper, more meaningful engagement. This ultimately leads to stronger and more effective connections with stakeholders.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Dec 19, 2025
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
Digital tools—dashboards, AI, and participatory platforms—boost transparency, two‑way communication, and cross‑sector collaboration for sustainability, but equity gaps persist.
Study: Impact of Technology on Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping how organizations connect with stakeholders to address sustainability challenges. By integrating digital tools like AI, data platforms, and participatory forums, companies improve transparency, enable two-way communication, and foster collaboration across sectors. Research shows that IT investments enhance engagement and drive measurable improvements in environmental, social, and economic outcomes. However, challenges such as the digital divide and underrepresentation of marginalized groups remain.
Key Takeaways:
Transparency: Real-time dashboards and data platforms build trust by providing accessible information.
Two-Way Communication: Digital tools empower stakeholders to give feedback and influence decisions.
Collaboration: Platforms streamline efforts across governments, NGOs, and businesses.
Challenges: Digital exclusion and a lack of long-term studies hinder progress.
Organizations must align IT investments with sustainability goals, design effective engagement processes, and act on stakeholder insights to achieve meaningful results.

Technology's Impact on Stakeholder Engagement and Sustainability Outcomes
The Importance of Stakeholder Engagement in Sustainability | Yale SOM


Research Overview: Findings and Methods
Exploring how technology influences stakeholder engagement in sustainability efforts involves a wide range of approaches and organizational settings. Studies have looked at the practices of multinational corporations, local governments, and nonprofits in managing various sustainability initiatives. These include large-scale projects in construction and energy sectors, where digital tools improve efficiency, as well as community-focused efforts that bring together companies, NGOs, and local authorities. Below, we break down the primary study categories, research methods, and key areas where further work is needed.
Study Categories
Researchers have taken different approaches to analyze the role of technology in sustainability:
Quantitative Models: These studies rely on survey data from industries like engineering, construction, and corporate management to explore the links between IT investments, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability outcomes.
Qualitative Case Studies: These focus on the dynamics of collaboration during sustainability transformations, shedding light on issues like power imbalances and challenges in creating inclusive processes.
Applied Evaluations: These examine the practical use of digital tools, such as social media for public consultations, data platforms for monitoring emissions, and collaborative software for coordinating efforts across sectors.
Research Methods Used
The methods employed in these studies are as varied as the questions they aim to answer:
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM): This statistical technique has been particularly effective in assessing the impact of IT investments on sustainability, with findings showing significant correlations [3].
Systematic Literature Reviews: These synthesize existing research on topics like "Digital CSR" and "Green IT", helping to establish theoretical foundations for how technology can enhance engagement.
Qualitative Approaches: Methods such as detailed case studies, participatory research involving stakeholders, and comparative analyses using frameworks like the five-pillar method (focusing on agency, system roles, power dynamics, problem alignment, and potential for transformation) provide deeper insights into the nuances of technology-enabled engagement.
While these methods have yielded valuable findings, there are still critical gaps in the research that need to be addressed.
Research Gaps
Despite the progress made, several limitations persist in this field of study:
Geographic Focus: Much of the existing research is centered on Western contexts, with limited attention to non-OECD regions and the Global South. This lack of diversity leaves out important perspectives and experiences.
Longitudinal Studies: Few studies examine the long-term effects of technology-enabled engagement, making it difficult to evaluate sustained outcomes over time.
Marginalized Stakeholders: Vulnerable and underrepresented groups are often overlooked, raising concerns about whether digital tools genuinely empower these communities or inadvertently exclude them.
Future research should address these gaps by exploring who benefits most from technology-driven engagement, particularly in contexts with significant power disparities. Doing so will help refine strategies for digital engagement and ensure more equitable and effective sustainability outcomes.
How Technology Changes Stakeholder Engagement
Technology is reshaping the way organizations engage with stakeholders in sustainability efforts. Gone are the days of relying solely on periodic reports or one-off public meetings. Today, digital platforms enable ongoing interaction, turning stakeholders into active participants. These tools allow stakeholders to monitor progress, provide feedback, and collaborate on solutions in real time. This shift is driving three key changes: greater transparency through accessible data, more dynamic two-way communication, and stronger cross-sector collaboration. Let’s explore how these changes are transforming stakeholder engagement.
Transparency and Information Access
Digital platforms are making transparency a cornerstone of stakeholder engagement. By offering direct access to sustainability data, these tools empower stakeholders to verify information themselves. Centralized dashboards and monitoring systems allow communities, investors, and regulators to track key metrics - like emissions, resource consumption, and project milestones - in real time. For instance, emissions tracking software and supply chain analysis tools provide a clear picture of environmental impact in relation to operational targets, building trust through verifiable data [4]. Organizations using real-time dashboards often report increased stakeholder confidence, especially when the data spans entire supply chains and highlights consistent progress toward sustainability goals.
Two-Way Communication
Digital tools like social media platforms, online consultations, and participatory forums are revolutionizing communication between organizations and stakeholders. Instead of one-way updates, companies can now engage in meaningful dialogue, gathering input and feedback from diverse groups. This approach not only keeps stakeholders informed but also empowers them to influence project decisions [2]. Platforms that facilitate participatory decision-making and stakeholder forums help integrate various perspectives, leading to policies that are more context-aware and widely supported. Research shows that strong stakeholder engagement, supported by effective two-way communication, improves sustainability outcomes and overall project performance [3]. By enabling continuous interaction, digital tools ensure stakeholders remain involved throughout a project’s lifecycle, rather than only at select stages.
Cross-Sector Collaboration
Digital platforms are also breaking down barriers between sectors, fostering collaboration among governments, NGOs, private companies, and local communities. These tools facilitate joint problem-solving and resource sharing through features like document sharing, real-time project tracking, and coordinated planning. This interconnected approach leverages collective expertise and resources, driving innovation and improving project outcomes [3][6].
The rise of cross-sector collaboration reflects a broader trend toward multi-stakeholder governance in sustainability initiatives. Networks that link customers, NGOs, and governments play a critical role in driving sustainability transitions. Policies from organizations like the Green Climate Fund now mandate the use of digital tools to ensure inclusive engagement [2]. Companies like Council Fire are helping organizations design and implement digital strategies that align financial, environmental, and social objectives. By integrating IT systems with stakeholder engagement, they’re enabling coordinated action across sectors in areas like energy, water, transportation, and sustainable community development.
Technology's Effect on Sustainability Results
The integration of digital tools into sustainability efforts is proving to be a game-changer, delivering measurable improvements across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research highlights that combining IT investments with stakeholder engagement leads to tangible progress, showing technology's critical role in driving sustainability outcomes [3][5]. Organizations that align their digital strategies with sustainability goals are reaping rewards such as lower emissions, stronger community relationships, and improved project performance. Let’s delve into the specific impacts on each dimension.
Environmental Results
Digital technologies are transforming environmental efforts by enabling real-time monitoring and more informed decision-making. For instance, AI-powered dashboards that track supply chain impacts allow businesses to identify and act on reduction opportunities, maximizing resource use while minimizing their environmental footprint [3][4]. Policies from groups like the Green Climate Fund now emphasize the use of tech-enabled consultations, combining local expertise with data insights to enhance emissions reduction and resource management efforts [2][4].
Virtual consultations, for example, cut down on travel-related emissions, while GIS mapping tools help stakeholders pinpoint areas for conservation and biodiversity protection. By giving stakeholders access to environmental data, these tools empower them to challenge outdated assumptions and spark green innovations that might otherwise go unnoticed [2][4].
Social Results
Technology is also reshaping social outcomes by expanding participation and fostering trust. Digital platforms, such as mobile-friendly tools and asynchronous forums, make it easier for people with non-traditional schedules, caregiving responsibilities, or mobility challenges to engage. Tools like GIS and data overlays further assist organizations in identifying underserved communities, ensuring equitable distribution of resources like green spaces and clean energy infrastructure.
By enhancing transparency, digital tools build trust through "closed-loop" communication, allowing stakeholders to see how their input influences decisions. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge. Economic inequalities and power imbalances can exclude marginalized groups from participating meaningfully. To address this, hybrid approaches that combine digital tools with traditional outreach methods are essential to ensure inclusive and authentic engagement [2][6].
Economic Results
Investments in IT are proving to be cost-effective while driving better project outcomes [3][5]. Digital platforms reduce the need for costly in-person meetings and manual processes by automating data collection and enabling virtual collaboration. They also help organizations detect stakeholder concerns early through sentiment analysis and real-time monitoring, minimizing risks like project delays, legal disputes, or community pushback.
When technology is strategically aligned with environmental and social goals, it becomes more than just a cost-saving tool - it becomes a competitive advantage. Studies applying the resource-based view show that organizations treating sustainability-focused IT - like monitoring systems and collaboration platforms - as strategic assets achieve stronger project results [3]. Stakeholder feedback gathered through these tools fosters resource efficiency and innovation, enhancing risk management and supporting overall success through collaborative engagement.
What Organizations Should Do
Research underscores a clear message: technology can deliver meaningful sustainability outcomes when it aligns with stakeholder engagement and environmental objectives. To achieve this, organizations must treat IT investments as tools for sustainability, create engagement processes that empower stakeholders, and turn insights into actionable projects. Here’s how they can make it happen:
Aligning IT Investments with Sustainability Goals
The first step is to identify the specific sustainability challenges and stakeholder needs before selecting the right technology. Too often, organizations jump straight to purchasing tools - such as dashboards or platforms - without fully understanding the problems they aim to solve or the people they intend to serve. When IT capabilities are directly tied to sustainability objectives, they evolve into strategic tools that can provide a competitive edge.
For example, integrated data systems that merge environmental, social, and economic performance into a single, comprehensive source of truth can be a game changer. Tools like emissions tracking software, which links supply chain data to business priorities, can transform vague climate commitments into actionable strategies [4]. These systems not only build stakeholder trust but also help meet reporting requirements. Still, despite 90% of organizations prioritizing sustainability in their tech modernization efforts, 54% report difficulties in achieving their ESG goals [4].
Specialized guidance from partners like Council Fire can also be invaluable. They assist organizations in merging financial performance with environmental and social outcomes through a mix of strategic advice and stakeholder collaboration. Their expertise can help pinpoint the most effective technology investments for areas like natural resource management, climate resilience, and sustainable infrastructure. Once the right tools are in place, organizations need to ensure that these investments are supported by effective engagement processes.
Designing Meaningful Engagement Processes
Engagement that feels tokenistic - where feedback is collected but doesn’t influence decisions - can erode trust. To prevent this, it’s important to define from the start which decisions will be shaped by stakeholder input and communicate those parameters clearly [2][6][7]. Structured stakeholder analysis can help identify who holds influence, agency, and alignment with the relevant issues, ensuring that digital tools like surveys, virtual workshops, participatory mapping, or mobile apps meet the needs of the people they are meant to serve.
According to the Global Reporting Initiative, 85% of organizations view stakeholder engagement as critical for effective risk management [2]. However, meaningful engagement requires more than just surveys. Organizations should implement "closed-loop" communication, showing stakeholders how their feedback has shaped project decisions. This could involve updates via online platforms or dashboards. Additionally, it’s important to address the digital divide by combining online and traditional outreach methods, such as phone calls, in-person meetings, or printed materials, to ensure that marginalized groups aren’t left out due to connectivity issues or low digital literacy.
Strong governance is essential to these efforts. Cross-functional teams - comprising representatives from sustainability, IT, operations, and communications - should oversee technology decisions, establish data standards, and ensure the quality of engagement efforts [4]. Clearly defining roles for managing stakeholder strategies, platforms, and ESG data is key, as is training staff to interpret sustainability analytics, facilitate online discussions, and translate complex data into easy-to-understand narratives [4][6]. With a solid engagement framework in place, organizations can focus on applying these insights to real-world projects.
Turning Insights into Actionable Projects
With IT aligned to sustainability goals and robust engagement strategies in place, organizations can use tools like GIS mapping and climate risk platforms in resilience planning. These technologies allow them to visualize hazards such as flooding or extreme heat, while inviting community input through interactive maps and virtual workshops [6][7]. For instance, creating portals where residents can submit resilience ideas, rank priorities, and track funding decisions can directly connect IT investments - like early warning systems or sensor networks - to the vulnerabilities identified by stakeholders.
A practical example of this approach comes from August 2016, when the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council, supported by Council Fire, used a stakeholder-driven risk assessment framework to apply ecosystem research to fisheries management. Facilitators like George Lapointe worked with stakeholders to identify and rank 12 key ecosystem elements. This collaboration led to the adoption of the Ecosystem Approach to Fisheries Management Guidance Document, which now governs 14 species by addressing high-risk interactions such as climate change and habitat loss.
In community development, studies show that IT investments can positively influence sustainability outcomes (effect size 0.175) [3]. By incorporating digital tools for participatory decision-making - such as real-time dashboards - organizations can empower employees and community members to better understand and improve their environmental and social impact. Piloting these technologies on a small scale, evaluating their effectiveness, and scaling up successful solutions can help bridge the gap between research and practical application.
Conclusion
Technology now plays a pivotal role in driving effective stakeholder engagement and advancing sustainability efforts. When organizations strategically align their IT investments with sustainability goals, they can achieve measurable benefits across environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Research underscores this connection, showing a statistically significant positive impact of IT investments on sustainability outcomes, reinforcing the notion that technology is indispensable for embedding sustainable practices into projects [3]. Additionally, stakeholder engagement has been shown to enhance sustainability performance, which subsequently improves overall project success [3]. However, challenges such as digital exclusion and inequities in participation remain significant barriers to fully realizing these benefits.
Despite technological advancements, a substantial digital divide persists. As of late 2023, about 33% of the global population - roughly 2.6 billion people - remained offline [1]. This stark reality highlights the limitations of digital-only strategies and underscores the importance of blending online tools with offline engagement methods. To address these gaps, organizations must adopt stakeholder analysis frameworks that consider power dynamics, ensuring that feedback mechanisms are meaningful and not merely procedural.
Future research must also address critical gaps in understanding. While existing studies affirm the link between IT, engagement, and sustainability, there is a lack of long-term analyses on digital engagement [6]. Equity-focused research and comparative studies across technologies, regions, and stakeholder groups will be essential for refining these insights and guiding future strategies.
For U.S. organizations, the urgency to align IT with sustainability is heightened by increasing regulatory demands, investor expectations, and community pressure regarding ESG and climate disclosures [4]. Council Fire exemplifies how organizations can integrate financial, environmental, and social performance through targeted strategies and stakeholder collaboration. By offering actionable roadmaps for sectors such as natural resource management, energy and water infrastructure, and sustainable communities, Council Fire demonstrates how expert guidance can translate research into impactful sustainability initiatives.
As technology continues to shape how organizations balance sustainability trade-offs, success will depend on strong governance, inclusive design, and a commitment to continuous improvement [4]. Moving forward, organizations must treat technology, stakeholder engagement, and sustainability as interconnected priorities. By investing in inclusive practices and fostering accountability, they can better navigate the complex challenges of sustainability and build trust with stakeholders [3]. Those that adopt this integrated approach will be well-equipped to tackle the pressing sustainability demands of the future.
FAQs
What can organizations do to bridge the digital divide in stakeholder engagement?
To address the digital divide in stakeholder engagement, organizations should prioritize inclusive communication by leveraging a mix of digital platforms tailored to reach diverse groups. Offering digital literacy training equips stakeholders with the skills to engage effectively, while ensuring affordable and dependable access to technology and internet connectivity promotes fair opportunities for participation. These efforts can lead to stronger collaboration and deeper connections with stakeholders.
How does aligning IT investments with sustainability goals benefit organizations?
Aligning IT investments with sustainability objectives allows organizations to establish deeper connections with stakeholders through openness, informed decision-making, and enhanced teamwork. These initiatives strengthen trust, improve communication, and lay the groundwork for lasting resilience and mutual growth.
Incorporating sustainability into IT strategies enables organizations to tackle environmental and social challenges more effectively while delivering measurable results that reflect their values and support their business goals.
How do digital tools improve communication and collaboration with stakeholders?
Digital tools have transformed the way organizations communicate and collaborate with their stakeholders, making interactions more immediate, open, and easy to access. With platforms like social media, video conferencing, and other collaborative tools, real-time discussions are now possible, which helps build trust and encourages active involvement.
These technologies simplify the feedback process, ensure updates are shared quickly, and open the door for deeper, more meaningful engagement. This ultimately leads to stronger and more effective connections with stakeholders.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
What makes Council Fire different?
Who does Council Fire you work with?
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


