


Jan 4, 2026
Jan 4, 2026
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Sustainability Strategy
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
GSTC's four pillars and certification guide tourism supply chains to reduce environmental harm, support communities, and measure impact.
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Global standards in tourism supply chains address challenges like unclear sustainability practices, fragmented eco-labels, and inconsistent impact measurement. The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) sets criteria across four key areas - management, social and economic effects, cultural preservation, and environmental impact - to create a unified framework for businesses, destinations, and tour operators. These guidelines help improve operations, support local communities, and reduce ecological harm while providing clear benchmarks for certification. Leading organizations like TUI Group and Marina Bay Sands have adopted these standards, demonstrating their value in improving transparency, accountability, and trust within the tourism sector. By aligning with GSTC standards, businesses can enhance their performance and credibility in a growing market for responsible travel.
GSTC2022: Influencing Supply Chains to be more Sustainable


The 4 Pillars of GSTC Standards
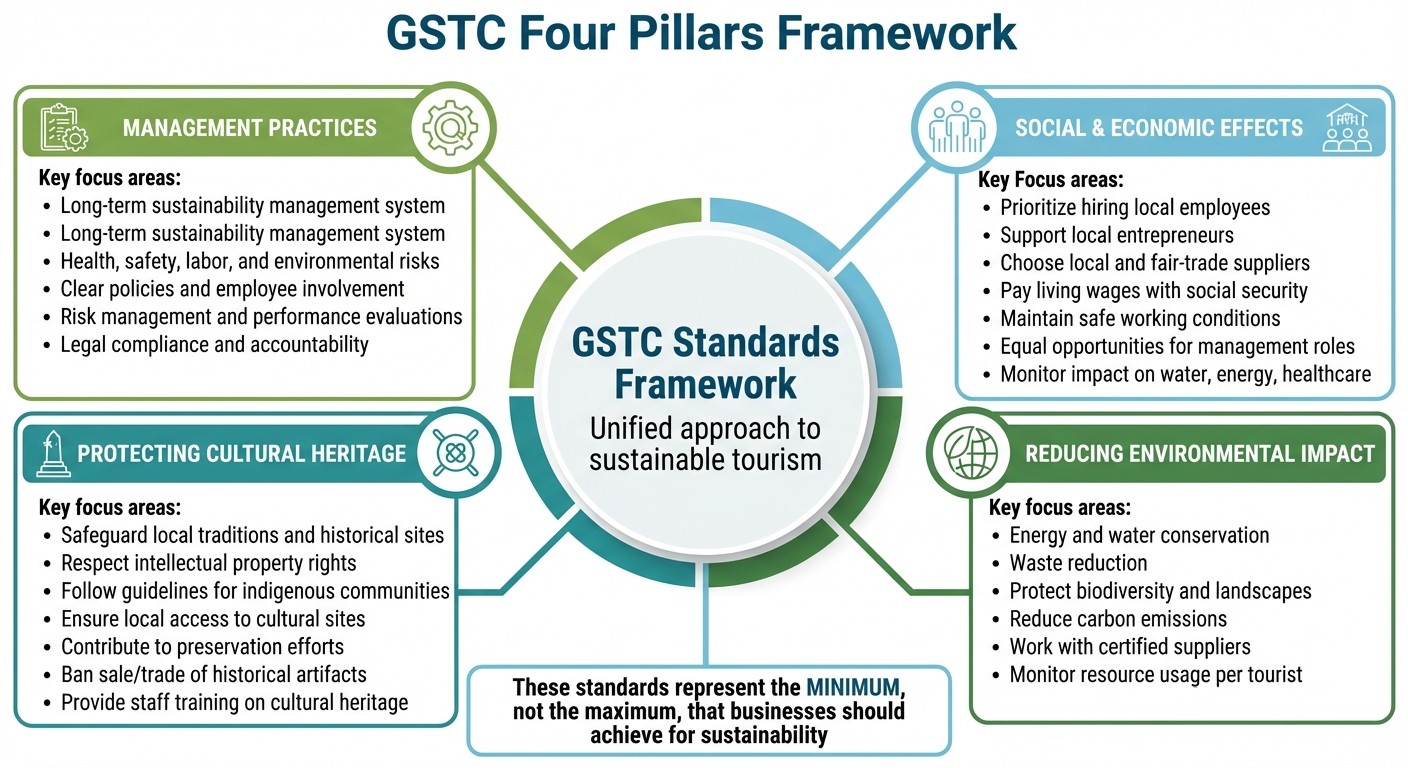
GSTC Four Pillars Framework for Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains
The GSTC Standards are built around four key pillars - Management, Socioeconomic, Cultural, and Environmental. These pillars establish a unified framework that allows tourism businesses to assess suppliers, monitor performance, and apply consistent sustainability practices throughout their supply chains [2][3]. Each pillar addresses a specific area of sustainability, working together to form a well-rounded approach. They also serve as the foundation for certification efforts and practical supply chain improvements.
Management Practices
The Sustainable Management pillar translates global sustainability criteria into actionable steps for businesses. It emphasizes the need for a long-term sustainability management system that tackles health, safety, labor, and environmental risks [3]. This system must be well-documented and cover environmental, social, cultural, and economic concerns across the organization. The aim is to foster continuous progress by implementing clear policies, involving employees at all levels, and ensuring compliance with legal standards. For supply chains, this means establishing oversight mechanisms, including risk management systems and regular performance evaluations. While the criteria set clear objectives, they allow businesses the flexibility to determine their own methods of implementation, ensuring both adaptability and accountability [3].
Social and Economic Effects
The Socioeconomic Impacts pillar focuses on maximizing benefits for local communities. It encourages businesses to prioritize hiring local employees, support local entrepreneurs, and choose local and fair-trade suppliers whenever possible [3]. To meet these goals, businesses are required to audit their supply chains to ensure they prioritize local sourcing, pay living wages, provide social security, and maintain safe working conditions. Additionally, local residents should have equal opportunities for management roles. Companies must also monitor their impact on essential local services such as water, energy, and healthcare, taking corrective steps if tourism activities threaten these resources.
Protecting Cultural Heritage
The Cultural Impacts pillar is dedicated to safeguarding and celebrating local traditions, historical sites, and spiritual landmarks while respecting intellectual property rights [3]. Tourism businesses must adhere to established guidelines when engaging with indigenous communities and culturally sensitive areas, ensuring that local residents benefit from these activities. Businesses are prohibited from restricting local access to cultural, historical, or spiritual sites and are expected to actively contribute to their preservation. The standards also regulate the use of historical artifacts, banning their sale or trade while requiring that any displays comply with local and international laws. To ensure respectful and accurate guest experiences, staff should receive periodic training on the area's cultural and natural heritage.
Reducing Environmental Impact
The Environmental Impacts pillar emphasizes efficient resource use, including energy and water conservation, waste reduction, and the protection of biodiversity and landscapes [3]. This pillar focuses on three core areas: resource consumption, pollution reduction (including carbon emissions), and the preservation of natural ecosystems [4]. Businesses are encouraged to work with certified suppliers and monitor energy and water usage per tourist [3]. As the GSTC explains, "The Standards are the minimum, not the maximum, which businesses, governments, and destinations should achieve to approach social, environmental, cultural, and economic sustainability" [4]. This statement underscores the importance of exceeding baseline requirements whenever possible. Together, these pillars guide actionable strategies for a more sustainable tourism supply chain.
Applying GSTC Standards to Tourism Supply Chains
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) provides a framework with specific sustainability guidelines tailored for hotels, tour operators, and destinations, ensuring a comprehensive approach to sustainable tourism.
Hotel and Accommodation Standards
The GSTC Hotel Standard outlines the essential criteria for accommodations to qualify as sustainable [6][7]. Hotels are required to implement long-term sustainability measures that address environmental, social, and economic concerns.
One key requirement, Criterion B3, emphasizes auditing supply chains and prioritizing local and fair-trade suppliers [6]. Leading hotel brands have already adopted GSTC standards to align their operations globally. For example, Hilton’s LightStay management system is designed to meet GSTC standards, as the company explains:
"We have aligned our LightStay management system with the criteria of the UN-founded Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC), the most respected seal of approval for sustainable travel and tourism practices" [1].
Similarly, Marina Bay Sands, the largest hotel in Singapore to achieve GSTC certification, reflects its dedication to sustainability. Meridith Beaujean, Executive Director of Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a testament to Marina Bay Sands' ongoing commitment to minimize our environmental impact while providing our guests with a luxurious experience" [1].
The framework also addresses infrastructure and operations. Criterion A7 encourages hotels to prioritize sustainable materials in planning and construction, such as using native plants and implementing efficient waste management systems. Additionally, regular staff training ensures employees understand their roles within the sustainability management system [6].
Tour operators face distinct challenges, and the GSTC provides clear standards to address these.
Tour Operator Standards
The GSTC Tour Operator Standard establishes guidelines for responsible supplier selection [8][9]. Operators are encouraged to work with suppliers - such as hotels, transportation providers, and excursion operators - that either hold GSTC certification or are actively pursuing it [9].
In 2021, MSC Cruises introduced a policy requiring its tour operators at frequent destinations to either be GSTC-certified or engaged in the certification process [1]. Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. also prioritizes GSTC-certified shore excursion operators through a preferential buying program. Stephanie DeMars, Corporate Responsibility Specialist at Royal Caribbean, highlighted:
"Taking WWF's recommendation of GSTC also simplified processes for RCL and promises to do the same for consumers" [1].
Tour operators are further encouraged to share the GSTC Industry Standard with their teams, fostering a collective understanding of sustainable practices. Management teams can also benefit from the GSTC Sustainable Tourism Training Program [9]. By December 30, 2025, operators will need to complete audits against specific mandatory indicators to ensure measurable sustainability goals are achieved [10].
These standards form the foundation for broader regional efforts under the Destination Standard.
Destination Standards
The GSTC Destination Standard provides a roadmap for regional sustainability efforts, emphasizing collaboration across sectors [11][12]. Destination managers play a key role by educating businesses about GSTC certification and promoting sustainable practices. Publicizing a list of sustainability-certified enterprises encourages local businesses to adopt global standards, while supporting local enterprises helps retain tourism revenue through sustainable investments [11].
Real-world examples demonstrate the impact of these standards. After a GSTC sustainability assessment, the St. Kitts Ministry of Tourism established the St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council. Diannille Taylor-Williams explained:
"The St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council was founded based on the principles of the GSTC Criteria for Destinations following St. Kitts and Nevis's GSTC destination sustainability assessment" [1].
In the U.S., Los Angeles became one of the first cities to join the GSTC. Adam Burke, President and CEO of the Los Angeles Tourism & Convention Board, expressed:
"We look forward to collaborating with GSTC and the Los Angeles City Tourism Department to build a thriving industry that improves the quality of life for all Angelenos" [1].
Destinations can also utilize tools like the GSTC Destination Self-Assessment Tool to evaluate progress in areas such as governance, socio-economic impact, cultural preservation, and environmental responsibility. The Destination Stewardship Starter Kit offers additional guidance for adopting a stewardship-oriented approach [12].
Certification and Performance Measurement
How GSTC Certification Works
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) operates by accrediting third-party Certification Bodies to conduct audits, ensuring compliance with its standards. This approach guarantees transparency, fairness, and expertise. As the GSTC clarifies:
"The term 'GSTC Certification' is a shorthand for 'Certified by a Certification Body that is GSTC-accredited.' ... GSTC does not certify directly, GSTC certifies the certifiers." [13]
The certification process involves a thorough review of documentation and on-site audits to confirm adherence to the GSTC’s four pillars. Certifications are generally valid for three years, though some programs, like Türkiye's Environmental and Cultural Sustainability Program, require annual renewals. In December 2025, Centara Hotels & Resorts became the first Thai hotel group to achieve full GSTC Certification for its entire portfolio. CEO Thirayuth Chirathivat credited the company’s "Centara EarthCare" framework, aligned with GSTC standards, as a key step before passing third-party audits. Similarly, by February 2025, The Ascott Limited reported that 25% of its managed and branded properties had achieved GSTC certification, with plans to reach 100% by 2028. This rigorous process ensures credibility and builds trust in sustainable tourism initiatives. [13]
Why Certification Matters for Supply Chains
Certification serves as a powerful tool for establishing trust and creating a competitive edge within supply chains. It provides verified proof of sustainability to travelers, corporate clients, and regulatory bodies, fulfilling requirements like those in the EU Green Claims directive. Research indicates that 53% of travelers actively seek accommodations featuring advanced sustainability practices, making certification a valuable differentiator. [13]
Leading hotel groups are setting ambitious sustainability goals. For instance, BWH Hotels has pledged to have all its branded properties certified by the end of 2026. In March 2025, Rosewood Hotel Group achieved GSTC certification across its portfolio. Mehvesh Mumtaz Ahmed, Vice President of Impact and Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a welcome endorsement that we are affixing this enrichment lens on every part of our business, from hiring, supply chain, and partnerships to procurement, design and more." [13]
GSTC certification also streamlines corporate procurement processes. It is recognized as the standard in the Global Business Travel Association's sustainable procurement guidelines for hotels and is often a mandatory criterion in corporate Request for Proposals (RFPs). Additionally, Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) and Travel Management Companies (TMCs) collaborate with GSTC through the Market Access Program (MAP) to spotlight certified accommodations to environmentally conscious travelers. [13]
Partnerships Supporting GSTC Standards
GSTC’s standards are bolstered by partnerships with prominent organizations, including the United Nations Foundation, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), UN Tourism, and the Rainforest Alliance. These collaborations enhance the credibility and impact of its certification process. [13] [5]
In November 2024, GSTC joined the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) as an Association Member, further strengthening its commitment to certification integrity. National tourism bodies in Türkiye, Singapore, and Malta have incorporated GSTC criteria into their regulations, shifting from voluntary guidelines to mandatory standards. [14] [13]
Support for GSTC standards continues to grow among industry leaders. Julia Simpson, President & CEO of the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), highlighted:
"Collaborating with an esteemed body like GSTC reinforces our dedication to leading the industry towards a more sustainable future. It's imperative that we work with key global players like GSTC to drive change, set benchmarks, and inspire others to follow." [1]
Conservation organizations, such as WWF, also back GSTC’s initiatives. In 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" holidays through 1,688 hotels certified to GSTC-recognized standards. Ian Corbett, Head of Sustainability at TUI Group, emphasized the importance of relying solely on certifications recognized by GSTC to meet the company’s stringent criteria. These partnerships, aligned with GSTC’s four pillars, play a crucial role in advancing sustainability across supply chains. [1]
How Council Fire Supports Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains

Implementing GSTC-Aligned Strategies
Council Fire takes the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) pillars and translates them into actionable strategies that drive real results. By helping tourism organizations integrate these pillars into their operations - whether managing hotels, tour services, or destination-wide initiatives - they go beyond simply meeting standards. Instead, they focus on achieving measurable goals that reflect genuine progress in sustainability.
Using a combination of systems thinking and data-driven approaches, Council Fire collaborates with governments, foundations, NGOs, and private companies. Their work emphasizes climate resilience, circular supply chains, and regenerative infrastructure, creating a foundation for impactful partnerships and meaningful stakeholder collaboration.
Building Partnerships Across Stakeholders
Sustainable tourism thrives on cooperation, and Council Fire plays a central role in bringing diverse stakeholders together. By fostering a shared understanding of sustainability through the GSTC Standards, they enable governments, businesses, and NGOs to align their policies and practices seamlessly [16][15][1].
Their approach adapts global standards to fit local realities, taking into account unique customs, laws, and conditions. Through trust-building and open dialogue, Council Fire helps bridge gaps between groups with differing priorities - whether it's hotel suppliers, community organizations, or local governments - ensuring everyone works together toward shared sustainability goals.
Using Data to Measure Supply Chain Performance
Council Fire employs the MST framework to create a unified way of measuring the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism supply chains [17]. This framework tracks critical metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions per visitor, water usage during overnight stays, and solid waste generation relative to tourism GDP.
The GSTC Standards act as the backbone of their evaluation process, providing a structured method for assessing performance across all four sustainability pillars [15]. By analyzing this data, Council Fire identifies actionable steps to reduce environmental harm, enhance social benefits, and safeguard cultural heritage. Their efforts ensure that tourism supply chains not only meet sustainability benchmarks but also excel in creating positive, lasting impacts.
Conclusion
The GSTC global standards serve as a unifying force for sustainability in tourism. They define the minimum baseline - not the ceiling - that businesses, governments, and destinations must meet to achieve real progress across environmental, social, and economic dimensions [2][3]. Without these standards, tourism supply chains would lack consistency, making it challenging to measure impact or drive collective improvement.
The GSTC's four pillars provide a well-rounded framework for meaningful change [2]. Adopting these standards creates resilient operations that support local communities, safeguard cultural heritage, and minimize environmental impact. For instance, in 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" vacations through 1,688 hotels certified under GSTC-recognized standards [1].
"With members spanning across the world, GSTC's rigorous accreditation program not only elevates our initiative but also ensures that the hospitality sector worldwide moves toward a unified vision of sustainability."
Julia Simpson, President & CEO, WTTC [1]
This accreditation underscores the importance of a shared framework for sustainability. Building on these global benchmarks, Council Fire translates standards into actionable strategies tailored to diverse stakeholders. By applying systems thinking and data-driven measurement, they enable tourism operations to achieve measurable progress. Their approach focuses on fostering partnerships, implementing circular supply chains, and tracking performance metrics to ensure lasting impact across the tourism sector.
Embracing GSTC standards positions tourism operations for enduring success, where sustainability becomes a cornerstone of competitive advantage and stakeholder confidence.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using GSTC standards for tourism businesses?
Adopting the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) standards equips tourism businesses with an internationally recognized framework to implement sustainable practices effectively. These standards guide businesses in refining their sustainability planning, boosting social and economic benefits for local communities, safeguarding cultural heritage, and minimizing environmental impacts. Grounded in rigorous, science-based benchmarks, they offer businesses a reliable way to demonstrate compliance to regulators, attract investors, and build trust with customers.
Aligning with GSTC standards also opens doors to the growing eco-conscious travel market, where sustainability certifications can justify premium pricing. By reducing waste, using resources more efficiently, and fostering stronger partnerships with local communities, businesses can achieve cost savings, enhance their reputation, and tap into broader market opportunities.
Council Fire, a consultancy specializing in sustainability, works with tourism operators to integrate GSTC standards into their strategies. This approach helps businesses achieve long-term success by balancing environmental, social, and financial priorities.
How do GSTC standards support the preservation of cultural heritage in tourism?
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) Standards highlight the importance of preserving cultural heritage as an integral part of sustainable tourism. These guidelines call on businesses, destinations, and attractions to protect cultural landmarks, encourage responsible visitor behavior, and honor local traditions and historical significance.
The standards provide a framework for operators to identify risks to cultural sites, create management plans to minimize the impact of tourism, and promote meaningful cultural interactions. By working closely with local communities and ensuring that tourism benefits are shared fairly, the GSTC framework aims to support tourism growth that respects and enriches cultural heritage. Council Fire collaborates with organizations to implement these principles through customized strategies that weave cultural preservation into sustainable tourism efforts.
Why is GSTC certification valuable for tourism supply chains?
GSTC certification plays a key role in shaping sustainable tourism supply chains by offering a globally acknowledged framework for responsible practices. It ensures that all contributors - whether they are hotels, tour operators, transportation services, or local attractions - embrace strategies that support environmental conservation, community welfare, cultural heritage, and operational transparency.
Achieving certification signals a strong dedication to sustainability, fostering trust among travelers, investors, and regulatory bodies. It also creates opportunities in the expanding market for eco-conscious travel, giving businesses a competitive edge. Beyond market advantages, aligning with GSTC standards helps organizations mitigate risks, cut compliance expenses, and protect their reputations by adhering to internationally recognized environmental and social benchmarks.
For businesses aiming to embed these standards into their operations, Council Fire offers specialized support. Their expertise simplifies the certification process, encourages collaboration, and transforms sustainability ambitions into measurable and profitable results, all while contributing positively to environmental and social well-being.
Related Blog Posts

Latest Articles
©2025
FAQ
FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Jan 4, 2026
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
GSTC's four pillars and certification guide tourism supply chains to reduce environmental harm, support communities, and measure impact.
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Global standards in tourism supply chains address challenges like unclear sustainability practices, fragmented eco-labels, and inconsistent impact measurement. The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) sets criteria across four key areas - management, social and economic effects, cultural preservation, and environmental impact - to create a unified framework for businesses, destinations, and tour operators. These guidelines help improve operations, support local communities, and reduce ecological harm while providing clear benchmarks for certification. Leading organizations like TUI Group and Marina Bay Sands have adopted these standards, demonstrating their value in improving transparency, accountability, and trust within the tourism sector. By aligning with GSTC standards, businesses can enhance their performance and credibility in a growing market for responsible travel.
GSTC2022: Influencing Supply Chains to be more Sustainable

The 4 Pillars of GSTC Standards


GSTC Four Pillars Framework for Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains
The GSTC Standards are built around four key pillars - Management, Socioeconomic, Cultural, and Environmental. These pillars establish a unified framework that allows tourism businesses to assess suppliers, monitor performance, and apply consistent sustainability practices throughout their supply chains [2][3]. Each pillar addresses a specific area of sustainability, working together to form a well-rounded approach. They also serve as the foundation for certification efforts and practical supply chain improvements.
Management Practices
The Sustainable Management pillar translates global sustainability criteria into actionable steps for businesses. It emphasizes the need for a long-term sustainability management system that tackles health, safety, labor, and environmental risks [3]. This system must be well-documented and cover environmental, social, cultural, and economic concerns across the organization. The aim is to foster continuous progress by implementing clear policies, involving employees at all levels, and ensuring compliance with legal standards. For supply chains, this means establishing oversight mechanisms, including risk management systems and regular performance evaluations. While the criteria set clear objectives, they allow businesses the flexibility to determine their own methods of implementation, ensuring both adaptability and accountability [3].
Social and Economic Effects
The Socioeconomic Impacts pillar focuses on maximizing benefits for local communities. It encourages businesses to prioritize hiring local employees, support local entrepreneurs, and choose local and fair-trade suppliers whenever possible [3]. To meet these goals, businesses are required to audit their supply chains to ensure they prioritize local sourcing, pay living wages, provide social security, and maintain safe working conditions. Additionally, local residents should have equal opportunities for management roles. Companies must also monitor their impact on essential local services such as water, energy, and healthcare, taking corrective steps if tourism activities threaten these resources.
Protecting Cultural Heritage
The Cultural Impacts pillar is dedicated to safeguarding and celebrating local traditions, historical sites, and spiritual landmarks while respecting intellectual property rights [3]. Tourism businesses must adhere to established guidelines when engaging with indigenous communities and culturally sensitive areas, ensuring that local residents benefit from these activities. Businesses are prohibited from restricting local access to cultural, historical, or spiritual sites and are expected to actively contribute to their preservation. The standards also regulate the use of historical artifacts, banning their sale or trade while requiring that any displays comply with local and international laws. To ensure respectful and accurate guest experiences, staff should receive periodic training on the area's cultural and natural heritage.
Reducing Environmental Impact
The Environmental Impacts pillar emphasizes efficient resource use, including energy and water conservation, waste reduction, and the protection of biodiversity and landscapes [3]. This pillar focuses on three core areas: resource consumption, pollution reduction (including carbon emissions), and the preservation of natural ecosystems [4]. Businesses are encouraged to work with certified suppliers and monitor energy and water usage per tourist [3]. As the GSTC explains, "The Standards are the minimum, not the maximum, which businesses, governments, and destinations should achieve to approach social, environmental, cultural, and economic sustainability" [4]. This statement underscores the importance of exceeding baseline requirements whenever possible. Together, these pillars guide actionable strategies for a more sustainable tourism supply chain.
Applying GSTC Standards to Tourism Supply Chains
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) provides a framework with specific sustainability guidelines tailored for hotels, tour operators, and destinations, ensuring a comprehensive approach to sustainable tourism.
Hotel and Accommodation Standards
The GSTC Hotel Standard outlines the essential criteria for accommodations to qualify as sustainable [6][7]. Hotels are required to implement long-term sustainability measures that address environmental, social, and economic concerns.
One key requirement, Criterion B3, emphasizes auditing supply chains and prioritizing local and fair-trade suppliers [6]. Leading hotel brands have already adopted GSTC standards to align their operations globally. For example, Hilton’s LightStay management system is designed to meet GSTC standards, as the company explains:
"We have aligned our LightStay management system with the criteria of the UN-founded Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC), the most respected seal of approval for sustainable travel and tourism practices" [1].
Similarly, Marina Bay Sands, the largest hotel in Singapore to achieve GSTC certification, reflects its dedication to sustainability. Meridith Beaujean, Executive Director of Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a testament to Marina Bay Sands' ongoing commitment to minimize our environmental impact while providing our guests with a luxurious experience" [1].
The framework also addresses infrastructure and operations. Criterion A7 encourages hotels to prioritize sustainable materials in planning and construction, such as using native plants and implementing efficient waste management systems. Additionally, regular staff training ensures employees understand their roles within the sustainability management system [6].
Tour operators face distinct challenges, and the GSTC provides clear standards to address these.
Tour Operator Standards
The GSTC Tour Operator Standard establishes guidelines for responsible supplier selection [8][9]. Operators are encouraged to work with suppliers - such as hotels, transportation providers, and excursion operators - that either hold GSTC certification or are actively pursuing it [9].
In 2021, MSC Cruises introduced a policy requiring its tour operators at frequent destinations to either be GSTC-certified or engaged in the certification process [1]. Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. also prioritizes GSTC-certified shore excursion operators through a preferential buying program. Stephanie DeMars, Corporate Responsibility Specialist at Royal Caribbean, highlighted:
"Taking WWF's recommendation of GSTC also simplified processes for RCL and promises to do the same for consumers" [1].
Tour operators are further encouraged to share the GSTC Industry Standard with their teams, fostering a collective understanding of sustainable practices. Management teams can also benefit from the GSTC Sustainable Tourism Training Program [9]. By December 30, 2025, operators will need to complete audits against specific mandatory indicators to ensure measurable sustainability goals are achieved [10].
These standards form the foundation for broader regional efforts under the Destination Standard.
Destination Standards
The GSTC Destination Standard provides a roadmap for regional sustainability efforts, emphasizing collaboration across sectors [11][12]. Destination managers play a key role by educating businesses about GSTC certification and promoting sustainable practices. Publicizing a list of sustainability-certified enterprises encourages local businesses to adopt global standards, while supporting local enterprises helps retain tourism revenue through sustainable investments [11].
Real-world examples demonstrate the impact of these standards. After a GSTC sustainability assessment, the St. Kitts Ministry of Tourism established the St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council. Diannille Taylor-Williams explained:
"The St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council was founded based on the principles of the GSTC Criteria for Destinations following St. Kitts and Nevis's GSTC destination sustainability assessment" [1].
In the U.S., Los Angeles became one of the first cities to join the GSTC. Adam Burke, President and CEO of the Los Angeles Tourism & Convention Board, expressed:
"We look forward to collaborating with GSTC and the Los Angeles City Tourism Department to build a thriving industry that improves the quality of life for all Angelenos" [1].
Destinations can also utilize tools like the GSTC Destination Self-Assessment Tool to evaluate progress in areas such as governance, socio-economic impact, cultural preservation, and environmental responsibility. The Destination Stewardship Starter Kit offers additional guidance for adopting a stewardship-oriented approach [12].
Certification and Performance Measurement
How GSTC Certification Works
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) operates by accrediting third-party Certification Bodies to conduct audits, ensuring compliance with its standards. This approach guarantees transparency, fairness, and expertise. As the GSTC clarifies:
"The term 'GSTC Certification' is a shorthand for 'Certified by a Certification Body that is GSTC-accredited.' ... GSTC does not certify directly, GSTC certifies the certifiers." [13]
The certification process involves a thorough review of documentation and on-site audits to confirm adherence to the GSTC’s four pillars. Certifications are generally valid for three years, though some programs, like Türkiye's Environmental and Cultural Sustainability Program, require annual renewals. In December 2025, Centara Hotels & Resorts became the first Thai hotel group to achieve full GSTC Certification for its entire portfolio. CEO Thirayuth Chirathivat credited the company’s "Centara EarthCare" framework, aligned with GSTC standards, as a key step before passing third-party audits. Similarly, by February 2025, The Ascott Limited reported that 25% of its managed and branded properties had achieved GSTC certification, with plans to reach 100% by 2028. This rigorous process ensures credibility and builds trust in sustainable tourism initiatives. [13]
Why Certification Matters for Supply Chains
Certification serves as a powerful tool for establishing trust and creating a competitive edge within supply chains. It provides verified proof of sustainability to travelers, corporate clients, and regulatory bodies, fulfilling requirements like those in the EU Green Claims directive. Research indicates that 53% of travelers actively seek accommodations featuring advanced sustainability practices, making certification a valuable differentiator. [13]
Leading hotel groups are setting ambitious sustainability goals. For instance, BWH Hotels has pledged to have all its branded properties certified by the end of 2026. In March 2025, Rosewood Hotel Group achieved GSTC certification across its portfolio. Mehvesh Mumtaz Ahmed, Vice President of Impact and Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a welcome endorsement that we are affixing this enrichment lens on every part of our business, from hiring, supply chain, and partnerships to procurement, design and more." [13]
GSTC certification also streamlines corporate procurement processes. It is recognized as the standard in the Global Business Travel Association's sustainable procurement guidelines for hotels and is often a mandatory criterion in corporate Request for Proposals (RFPs). Additionally, Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) and Travel Management Companies (TMCs) collaborate with GSTC through the Market Access Program (MAP) to spotlight certified accommodations to environmentally conscious travelers. [13]
Partnerships Supporting GSTC Standards
GSTC’s standards are bolstered by partnerships with prominent organizations, including the United Nations Foundation, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), UN Tourism, and the Rainforest Alliance. These collaborations enhance the credibility and impact of its certification process. [13] [5]
In November 2024, GSTC joined the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) as an Association Member, further strengthening its commitment to certification integrity. National tourism bodies in Türkiye, Singapore, and Malta have incorporated GSTC criteria into their regulations, shifting from voluntary guidelines to mandatory standards. [14] [13]
Support for GSTC standards continues to grow among industry leaders. Julia Simpson, President & CEO of the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), highlighted:
"Collaborating with an esteemed body like GSTC reinforces our dedication to leading the industry towards a more sustainable future. It's imperative that we work with key global players like GSTC to drive change, set benchmarks, and inspire others to follow." [1]
Conservation organizations, such as WWF, also back GSTC’s initiatives. In 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" holidays through 1,688 hotels certified to GSTC-recognized standards. Ian Corbett, Head of Sustainability at TUI Group, emphasized the importance of relying solely on certifications recognized by GSTC to meet the company’s stringent criteria. These partnerships, aligned with GSTC’s four pillars, play a crucial role in advancing sustainability across supply chains. [1]
How Council Fire Supports Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains

Implementing GSTC-Aligned Strategies
Council Fire takes the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) pillars and translates them into actionable strategies that drive real results. By helping tourism organizations integrate these pillars into their operations - whether managing hotels, tour services, or destination-wide initiatives - they go beyond simply meeting standards. Instead, they focus on achieving measurable goals that reflect genuine progress in sustainability.
Using a combination of systems thinking and data-driven approaches, Council Fire collaborates with governments, foundations, NGOs, and private companies. Their work emphasizes climate resilience, circular supply chains, and regenerative infrastructure, creating a foundation for impactful partnerships and meaningful stakeholder collaboration.
Building Partnerships Across Stakeholders
Sustainable tourism thrives on cooperation, and Council Fire plays a central role in bringing diverse stakeholders together. By fostering a shared understanding of sustainability through the GSTC Standards, they enable governments, businesses, and NGOs to align their policies and practices seamlessly [16][15][1].
Their approach adapts global standards to fit local realities, taking into account unique customs, laws, and conditions. Through trust-building and open dialogue, Council Fire helps bridge gaps between groups with differing priorities - whether it's hotel suppliers, community organizations, or local governments - ensuring everyone works together toward shared sustainability goals.
Using Data to Measure Supply Chain Performance
Council Fire employs the MST framework to create a unified way of measuring the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism supply chains [17]. This framework tracks critical metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions per visitor, water usage during overnight stays, and solid waste generation relative to tourism GDP.
The GSTC Standards act as the backbone of their evaluation process, providing a structured method for assessing performance across all four sustainability pillars [15]. By analyzing this data, Council Fire identifies actionable steps to reduce environmental harm, enhance social benefits, and safeguard cultural heritage. Their efforts ensure that tourism supply chains not only meet sustainability benchmarks but also excel in creating positive, lasting impacts.
Conclusion
The GSTC global standards serve as a unifying force for sustainability in tourism. They define the minimum baseline - not the ceiling - that businesses, governments, and destinations must meet to achieve real progress across environmental, social, and economic dimensions [2][3]. Without these standards, tourism supply chains would lack consistency, making it challenging to measure impact or drive collective improvement.
The GSTC's four pillars provide a well-rounded framework for meaningful change [2]. Adopting these standards creates resilient operations that support local communities, safeguard cultural heritage, and minimize environmental impact. For instance, in 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" vacations through 1,688 hotels certified under GSTC-recognized standards [1].
"With members spanning across the world, GSTC's rigorous accreditation program not only elevates our initiative but also ensures that the hospitality sector worldwide moves toward a unified vision of sustainability."
Julia Simpson, President & CEO, WTTC [1]
This accreditation underscores the importance of a shared framework for sustainability. Building on these global benchmarks, Council Fire translates standards into actionable strategies tailored to diverse stakeholders. By applying systems thinking and data-driven measurement, they enable tourism operations to achieve measurable progress. Their approach focuses on fostering partnerships, implementing circular supply chains, and tracking performance metrics to ensure lasting impact across the tourism sector.
Embracing GSTC standards positions tourism operations for enduring success, where sustainability becomes a cornerstone of competitive advantage and stakeholder confidence.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using GSTC standards for tourism businesses?
Adopting the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) standards equips tourism businesses with an internationally recognized framework to implement sustainable practices effectively. These standards guide businesses in refining their sustainability planning, boosting social and economic benefits for local communities, safeguarding cultural heritage, and minimizing environmental impacts. Grounded in rigorous, science-based benchmarks, they offer businesses a reliable way to demonstrate compliance to regulators, attract investors, and build trust with customers.
Aligning with GSTC standards also opens doors to the growing eco-conscious travel market, where sustainability certifications can justify premium pricing. By reducing waste, using resources more efficiently, and fostering stronger partnerships with local communities, businesses can achieve cost savings, enhance their reputation, and tap into broader market opportunities.
Council Fire, a consultancy specializing in sustainability, works with tourism operators to integrate GSTC standards into their strategies. This approach helps businesses achieve long-term success by balancing environmental, social, and financial priorities.
How do GSTC standards support the preservation of cultural heritage in tourism?
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) Standards highlight the importance of preserving cultural heritage as an integral part of sustainable tourism. These guidelines call on businesses, destinations, and attractions to protect cultural landmarks, encourage responsible visitor behavior, and honor local traditions and historical significance.
The standards provide a framework for operators to identify risks to cultural sites, create management plans to minimize the impact of tourism, and promote meaningful cultural interactions. By working closely with local communities and ensuring that tourism benefits are shared fairly, the GSTC framework aims to support tourism growth that respects and enriches cultural heritage. Council Fire collaborates with organizations to implement these principles through customized strategies that weave cultural preservation into sustainable tourism efforts.
Why is GSTC certification valuable for tourism supply chains?
GSTC certification plays a key role in shaping sustainable tourism supply chains by offering a globally acknowledged framework for responsible practices. It ensures that all contributors - whether they are hotels, tour operators, transportation services, or local attractions - embrace strategies that support environmental conservation, community welfare, cultural heritage, and operational transparency.
Achieving certification signals a strong dedication to sustainability, fostering trust among travelers, investors, and regulatory bodies. It also creates opportunities in the expanding market for eco-conscious travel, giving businesses a competitive edge. Beyond market advantages, aligning with GSTC standards helps organizations mitigate risks, cut compliance expenses, and protect their reputations by adhering to internationally recognized environmental and social benchmarks.
For businesses aiming to embed these standards into their operations, Council Fire offers specialized support. Their expertise simplifies the certification process, encourages collaboration, and transforms sustainability ambitions into measurable and profitable results, all while contributing positively to environmental and social well-being.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
01
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
02
What makes Council Fire different?
03
Who does Council Fire you work with?
04
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
05
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
06
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


Jan 4, 2026
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Sustainability Strategy
In This Article
GSTC's four pillars and certification guide tourism supply chains to reduce environmental harm, support communities, and measure impact.
Global Standards for Tourism Supply Chains
Global standards in tourism supply chains address challenges like unclear sustainability practices, fragmented eco-labels, and inconsistent impact measurement. The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) sets criteria across four key areas - management, social and economic effects, cultural preservation, and environmental impact - to create a unified framework for businesses, destinations, and tour operators. These guidelines help improve operations, support local communities, and reduce ecological harm while providing clear benchmarks for certification. Leading organizations like TUI Group and Marina Bay Sands have adopted these standards, demonstrating their value in improving transparency, accountability, and trust within the tourism sector. By aligning with GSTC standards, businesses can enhance their performance and credibility in a growing market for responsible travel.
GSTC2022: Influencing Supply Chains to be more Sustainable

The 4 Pillars of GSTC Standards


GSTC Four Pillars Framework for Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains
The GSTC Standards are built around four key pillars - Management, Socioeconomic, Cultural, and Environmental. These pillars establish a unified framework that allows tourism businesses to assess suppliers, monitor performance, and apply consistent sustainability practices throughout their supply chains [2][3]. Each pillar addresses a specific area of sustainability, working together to form a well-rounded approach. They also serve as the foundation for certification efforts and practical supply chain improvements.
Management Practices
The Sustainable Management pillar translates global sustainability criteria into actionable steps for businesses. It emphasizes the need for a long-term sustainability management system that tackles health, safety, labor, and environmental risks [3]. This system must be well-documented and cover environmental, social, cultural, and economic concerns across the organization. The aim is to foster continuous progress by implementing clear policies, involving employees at all levels, and ensuring compliance with legal standards. For supply chains, this means establishing oversight mechanisms, including risk management systems and regular performance evaluations. While the criteria set clear objectives, they allow businesses the flexibility to determine their own methods of implementation, ensuring both adaptability and accountability [3].
Social and Economic Effects
The Socioeconomic Impacts pillar focuses on maximizing benefits for local communities. It encourages businesses to prioritize hiring local employees, support local entrepreneurs, and choose local and fair-trade suppliers whenever possible [3]. To meet these goals, businesses are required to audit their supply chains to ensure they prioritize local sourcing, pay living wages, provide social security, and maintain safe working conditions. Additionally, local residents should have equal opportunities for management roles. Companies must also monitor their impact on essential local services such as water, energy, and healthcare, taking corrective steps if tourism activities threaten these resources.
Protecting Cultural Heritage
The Cultural Impacts pillar is dedicated to safeguarding and celebrating local traditions, historical sites, and spiritual landmarks while respecting intellectual property rights [3]. Tourism businesses must adhere to established guidelines when engaging with indigenous communities and culturally sensitive areas, ensuring that local residents benefit from these activities. Businesses are prohibited from restricting local access to cultural, historical, or spiritual sites and are expected to actively contribute to their preservation. The standards also regulate the use of historical artifacts, banning their sale or trade while requiring that any displays comply with local and international laws. To ensure respectful and accurate guest experiences, staff should receive periodic training on the area's cultural and natural heritage.
Reducing Environmental Impact
The Environmental Impacts pillar emphasizes efficient resource use, including energy and water conservation, waste reduction, and the protection of biodiversity and landscapes [3]. This pillar focuses on three core areas: resource consumption, pollution reduction (including carbon emissions), and the preservation of natural ecosystems [4]. Businesses are encouraged to work with certified suppliers and monitor energy and water usage per tourist [3]. As the GSTC explains, "The Standards are the minimum, not the maximum, which businesses, governments, and destinations should achieve to approach social, environmental, cultural, and economic sustainability" [4]. This statement underscores the importance of exceeding baseline requirements whenever possible. Together, these pillars guide actionable strategies for a more sustainable tourism supply chain.
Applying GSTC Standards to Tourism Supply Chains
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) provides a framework with specific sustainability guidelines tailored for hotels, tour operators, and destinations, ensuring a comprehensive approach to sustainable tourism.
Hotel and Accommodation Standards
The GSTC Hotel Standard outlines the essential criteria for accommodations to qualify as sustainable [6][7]. Hotels are required to implement long-term sustainability measures that address environmental, social, and economic concerns.
One key requirement, Criterion B3, emphasizes auditing supply chains and prioritizing local and fair-trade suppliers [6]. Leading hotel brands have already adopted GSTC standards to align their operations globally. For example, Hilton’s LightStay management system is designed to meet GSTC standards, as the company explains:
"We have aligned our LightStay management system with the criteria of the UN-founded Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC), the most respected seal of approval for sustainable travel and tourism practices" [1].
Similarly, Marina Bay Sands, the largest hotel in Singapore to achieve GSTC certification, reflects its dedication to sustainability. Meridith Beaujean, Executive Director of Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a testament to Marina Bay Sands' ongoing commitment to minimize our environmental impact while providing our guests with a luxurious experience" [1].
The framework also addresses infrastructure and operations. Criterion A7 encourages hotels to prioritize sustainable materials in planning and construction, such as using native plants and implementing efficient waste management systems. Additionally, regular staff training ensures employees understand their roles within the sustainability management system [6].
Tour operators face distinct challenges, and the GSTC provides clear standards to address these.
Tour Operator Standards
The GSTC Tour Operator Standard establishes guidelines for responsible supplier selection [8][9]. Operators are encouraged to work with suppliers - such as hotels, transportation providers, and excursion operators - that either hold GSTC certification or are actively pursuing it [9].
In 2021, MSC Cruises introduced a policy requiring its tour operators at frequent destinations to either be GSTC-certified or engaged in the certification process [1]. Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. also prioritizes GSTC-certified shore excursion operators through a preferential buying program. Stephanie DeMars, Corporate Responsibility Specialist at Royal Caribbean, highlighted:
"Taking WWF's recommendation of GSTC also simplified processes for RCL and promises to do the same for consumers" [1].
Tour operators are further encouraged to share the GSTC Industry Standard with their teams, fostering a collective understanding of sustainable practices. Management teams can also benefit from the GSTC Sustainable Tourism Training Program [9]. By December 30, 2025, operators will need to complete audits against specific mandatory indicators to ensure measurable sustainability goals are achieved [10].
These standards form the foundation for broader regional efforts under the Destination Standard.
Destination Standards
The GSTC Destination Standard provides a roadmap for regional sustainability efforts, emphasizing collaboration across sectors [11][12]. Destination managers play a key role by educating businesses about GSTC certification and promoting sustainable practices. Publicizing a list of sustainability-certified enterprises encourages local businesses to adopt global standards, while supporting local enterprises helps retain tourism revenue through sustainable investments [11].
Real-world examples demonstrate the impact of these standards. After a GSTC sustainability assessment, the St. Kitts Ministry of Tourism established the St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council. Diannille Taylor-Williams explained:
"The St. Kitts Sustainable Destination Council was founded based on the principles of the GSTC Criteria for Destinations following St. Kitts and Nevis's GSTC destination sustainability assessment" [1].
In the U.S., Los Angeles became one of the first cities to join the GSTC. Adam Burke, President and CEO of the Los Angeles Tourism & Convention Board, expressed:
"We look forward to collaborating with GSTC and the Los Angeles City Tourism Department to build a thriving industry that improves the quality of life for all Angelenos" [1].
Destinations can also utilize tools like the GSTC Destination Self-Assessment Tool to evaluate progress in areas such as governance, socio-economic impact, cultural preservation, and environmental responsibility. The Destination Stewardship Starter Kit offers additional guidance for adopting a stewardship-oriented approach [12].
Certification and Performance Measurement
How GSTC Certification Works
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) operates by accrediting third-party Certification Bodies to conduct audits, ensuring compliance with its standards. This approach guarantees transparency, fairness, and expertise. As the GSTC clarifies:
"The term 'GSTC Certification' is a shorthand for 'Certified by a Certification Body that is GSTC-accredited.' ... GSTC does not certify directly, GSTC certifies the certifiers." [13]
The certification process involves a thorough review of documentation and on-site audits to confirm adherence to the GSTC’s four pillars. Certifications are generally valid for three years, though some programs, like Türkiye's Environmental and Cultural Sustainability Program, require annual renewals. In December 2025, Centara Hotels & Resorts became the first Thai hotel group to achieve full GSTC Certification for its entire portfolio. CEO Thirayuth Chirathivat credited the company’s "Centara EarthCare" framework, aligned with GSTC standards, as a key step before passing third-party audits. Similarly, by February 2025, The Ascott Limited reported that 25% of its managed and branded properties had achieved GSTC certification, with plans to reach 100% by 2028. This rigorous process ensures credibility and builds trust in sustainable tourism initiatives. [13]
Why Certification Matters for Supply Chains
Certification serves as a powerful tool for establishing trust and creating a competitive edge within supply chains. It provides verified proof of sustainability to travelers, corporate clients, and regulatory bodies, fulfilling requirements like those in the EU Green Claims directive. Research indicates that 53% of travelers actively seek accommodations featuring advanced sustainability practices, making certification a valuable differentiator. [13]
Leading hotel groups are setting ambitious sustainability goals. For instance, BWH Hotels has pledged to have all its branded properties certified by the end of 2026. In March 2025, Rosewood Hotel Group achieved GSTC certification across its portfolio. Mehvesh Mumtaz Ahmed, Vice President of Impact and Sustainability, remarked:
"The GSTC certification is a welcome endorsement that we are affixing this enrichment lens on every part of our business, from hiring, supply chain, and partnerships to procurement, design and more." [13]
GSTC certification also streamlines corporate procurement processes. It is recognized as the standard in the Global Business Travel Association's sustainable procurement guidelines for hotels and is often a mandatory criterion in corporate Request for Proposals (RFPs). Additionally, Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) and Travel Management Companies (TMCs) collaborate with GSTC through the Market Access Program (MAP) to spotlight certified accommodations to environmentally conscious travelers. [13]
Partnerships Supporting GSTC Standards
GSTC’s standards are bolstered by partnerships with prominent organizations, including the United Nations Foundation, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), UN Tourism, and the Rainforest Alliance. These collaborations enhance the credibility and impact of its certification process. [13] [5]
In November 2024, GSTC joined the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) as an Association Member, further strengthening its commitment to certification integrity. National tourism bodies in Türkiye, Singapore, and Malta have incorporated GSTC criteria into their regulations, shifting from voluntary guidelines to mandatory standards. [14] [13]
Support for GSTC standards continues to grow among industry leaders. Julia Simpson, President & CEO of the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), highlighted:
"Collaborating with an esteemed body like GSTC reinforces our dedication to leading the industry towards a more sustainable future. It's imperative that we work with key global players like GSTC to drive change, set benchmarks, and inspire others to follow." [1]
Conservation organizations, such as WWF, also back GSTC’s initiatives. In 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" holidays through 1,688 hotels certified to GSTC-recognized standards. Ian Corbett, Head of Sustainability at TUI Group, emphasized the importance of relying solely on certifications recognized by GSTC to meet the company’s stringent criteria. These partnerships, aligned with GSTC’s four pillars, play a crucial role in advancing sustainability across supply chains. [1]
How Council Fire Supports Sustainable Tourism Supply Chains

Implementing GSTC-Aligned Strategies
Council Fire takes the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) pillars and translates them into actionable strategies that drive real results. By helping tourism organizations integrate these pillars into their operations - whether managing hotels, tour services, or destination-wide initiatives - they go beyond simply meeting standards. Instead, they focus on achieving measurable goals that reflect genuine progress in sustainability.
Using a combination of systems thinking and data-driven approaches, Council Fire collaborates with governments, foundations, NGOs, and private companies. Their work emphasizes climate resilience, circular supply chains, and regenerative infrastructure, creating a foundation for impactful partnerships and meaningful stakeholder collaboration.
Building Partnerships Across Stakeholders
Sustainable tourism thrives on cooperation, and Council Fire plays a central role in bringing diverse stakeholders together. By fostering a shared understanding of sustainability through the GSTC Standards, they enable governments, businesses, and NGOs to align their policies and practices seamlessly [16][15][1].
Their approach adapts global standards to fit local realities, taking into account unique customs, laws, and conditions. Through trust-building and open dialogue, Council Fire helps bridge gaps between groups with differing priorities - whether it's hotel suppliers, community organizations, or local governments - ensuring everyone works together toward shared sustainability goals.
Using Data to Measure Supply Chain Performance
Council Fire employs the MST framework to create a unified way of measuring the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism supply chains [17]. This framework tracks critical metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions per visitor, water usage during overnight stays, and solid waste generation relative to tourism GDP.
The GSTC Standards act as the backbone of their evaluation process, providing a structured method for assessing performance across all four sustainability pillars [15]. By analyzing this data, Council Fire identifies actionable steps to reduce environmental harm, enhance social benefits, and safeguard cultural heritage. Their efforts ensure that tourism supply chains not only meet sustainability benchmarks but also excel in creating positive, lasting impacts.
Conclusion
The GSTC global standards serve as a unifying force for sustainability in tourism. They define the minimum baseline - not the ceiling - that businesses, governments, and destinations must meet to achieve real progress across environmental, social, and economic dimensions [2][3]. Without these standards, tourism supply chains would lack consistency, making it challenging to measure impact or drive collective improvement.
The GSTC's four pillars provide a well-rounded framework for meaningful change [2]. Adopting these standards creates resilient operations that support local communities, safeguard cultural heritage, and minimize environmental impact. For instance, in 2019, TUI Group facilitated 10.3 million "greener and fairer" vacations through 1,688 hotels certified under GSTC-recognized standards [1].
"With members spanning across the world, GSTC's rigorous accreditation program not only elevates our initiative but also ensures that the hospitality sector worldwide moves toward a unified vision of sustainability."
Julia Simpson, President & CEO, WTTC [1]
This accreditation underscores the importance of a shared framework for sustainability. Building on these global benchmarks, Council Fire translates standards into actionable strategies tailored to diverse stakeholders. By applying systems thinking and data-driven measurement, they enable tourism operations to achieve measurable progress. Their approach focuses on fostering partnerships, implementing circular supply chains, and tracking performance metrics to ensure lasting impact across the tourism sector.
Embracing GSTC standards positions tourism operations for enduring success, where sustainability becomes a cornerstone of competitive advantage and stakeholder confidence.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using GSTC standards for tourism businesses?
Adopting the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) standards equips tourism businesses with an internationally recognized framework to implement sustainable practices effectively. These standards guide businesses in refining their sustainability planning, boosting social and economic benefits for local communities, safeguarding cultural heritage, and minimizing environmental impacts. Grounded in rigorous, science-based benchmarks, they offer businesses a reliable way to demonstrate compliance to regulators, attract investors, and build trust with customers.
Aligning with GSTC standards also opens doors to the growing eco-conscious travel market, where sustainability certifications can justify premium pricing. By reducing waste, using resources more efficiently, and fostering stronger partnerships with local communities, businesses can achieve cost savings, enhance their reputation, and tap into broader market opportunities.
Council Fire, a consultancy specializing in sustainability, works with tourism operators to integrate GSTC standards into their strategies. This approach helps businesses achieve long-term success by balancing environmental, social, and financial priorities.
How do GSTC standards support the preservation of cultural heritage in tourism?
The Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) Standards highlight the importance of preserving cultural heritage as an integral part of sustainable tourism. These guidelines call on businesses, destinations, and attractions to protect cultural landmarks, encourage responsible visitor behavior, and honor local traditions and historical significance.
The standards provide a framework for operators to identify risks to cultural sites, create management plans to minimize the impact of tourism, and promote meaningful cultural interactions. By working closely with local communities and ensuring that tourism benefits are shared fairly, the GSTC framework aims to support tourism growth that respects and enriches cultural heritage. Council Fire collaborates with organizations to implement these principles through customized strategies that weave cultural preservation into sustainable tourism efforts.
Why is GSTC certification valuable for tourism supply chains?
GSTC certification plays a key role in shaping sustainable tourism supply chains by offering a globally acknowledged framework for responsible practices. It ensures that all contributors - whether they are hotels, tour operators, transportation services, or local attractions - embrace strategies that support environmental conservation, community welfare, cultural heritage, and operational transparency.
Achieving certification signals a strong dedication to sustainability, fostering trust among travelers, investors, and regulatory bodies. It also creates opportunities in the expanding market for eco-conscious travel, giving businesses a competitive edge. Beyond market advantages, aligning with GSTC standards helps organizations mitigate risks, cut compliance expenses, and protect their reputations by adhering to internationally recognized environmental and social benchmarks.
For businesses aiming to embed these standards into their operations, Council Fire offers specialized support. Their expertise simplifies the certification process, encourages collaboration, and transforms sustainability ambitions into measurable and profitable results, all while contributing positively to environmental and social well-being.
Related Blog Posts

FAQ
What does it really mean to “redefine profit”?
What makes Council Fire different?
Who does Council Fire you work with?
What does working with Council Fire actually look like?
How does Council Fire help organizations turn big goals into action?
How does Council Fire define and measure success?


